NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry – Here are all the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8. This solution contains questions, answers, images, explanations of the complete Chapter 8 titled Introduction to Trigonometry of Maths taught in Class 10. If you are a student of Class 10 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Maths, then you must come across Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry. After you have studied lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry in one place.
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
Here on AglaSem Schools, you can access to NCERT Book Solutions in free pdf for Maths for Class 10 so that you can refer them as and when required. The NCERT Solutions to the questions after every unit of NCERT textbooks aimed at helping students solving difficult questions.
For a better understanding of this chapter, you should also see summary of Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry , Maths, Class 10.
| Class | 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Book | Mathematics |
| Chapter Number | 8 |
| Chapter Name |
Introduction to Trigonometry |
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
Class 10, Maths chapter 8, Introduction to Trigonometry solutions are given below in PDF format. You can view them online or download PDF file for future use.
Introduction to Trigonometry Download
Did you find NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry helpful? If yes, please comment below. Also please like, and share it with your friends!
NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry- Video
You can also watch the video solutions of NCERT Class10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry here.
If you liked the video, please subscribe to our YouTube channel so that you can get more such interesting and useful study resources.
Download NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry In PDF Format
You can also download here the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry in PDF format.
Click Here to download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
Question & Answer
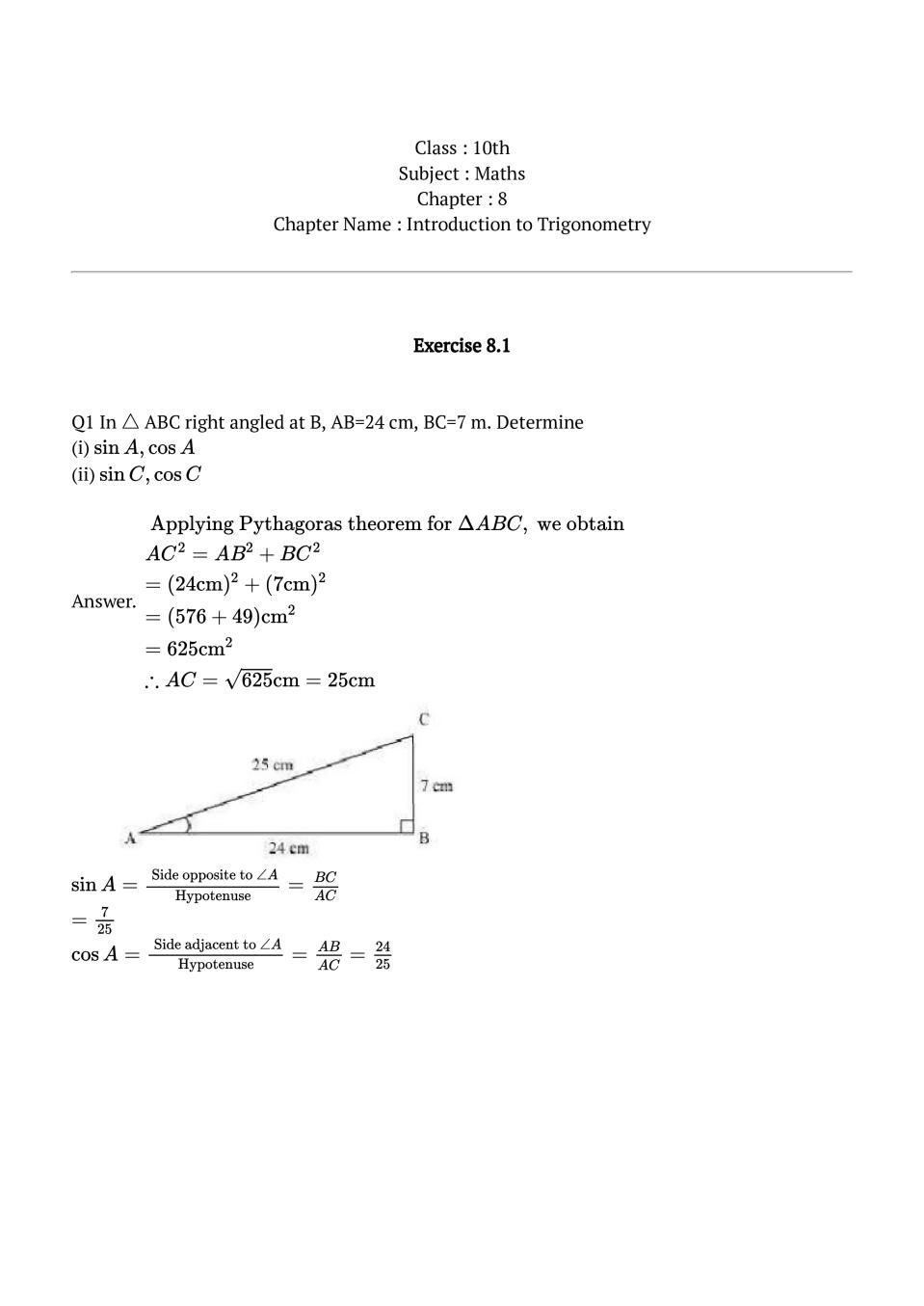
Q.1: In \(\triangle\) ABC right angled at B, AB=24 cm, BC=7 m. Determine
(i) \(\sin A, \cos A\)
(ii) \(\sin C, \cos C\)
Ans : \(\begin{array}{l}{\text { Applying Pythagoras theorem for } \Delta A B C, \text { we obtain }} \\ {A C^{2}=A B^{2}+B C^{2}} \\ {=(24 \mathrm{cm})^{2}+(7 \mathrm{cm})^{2}} \\ {=(576+49) \mathrm{cm}^{2}} \\ {=625 \mathrm{cm}^{2}} \\ {\therefore A C=\sqrt{625} \mathrm{cm}=25 \mathrm{cm}}\end{array}\)\(\sin A=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle A}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{B C}{A C}\) \(=\frac{7}{25}\) \(\cos A=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{24}{25}\) (ii)
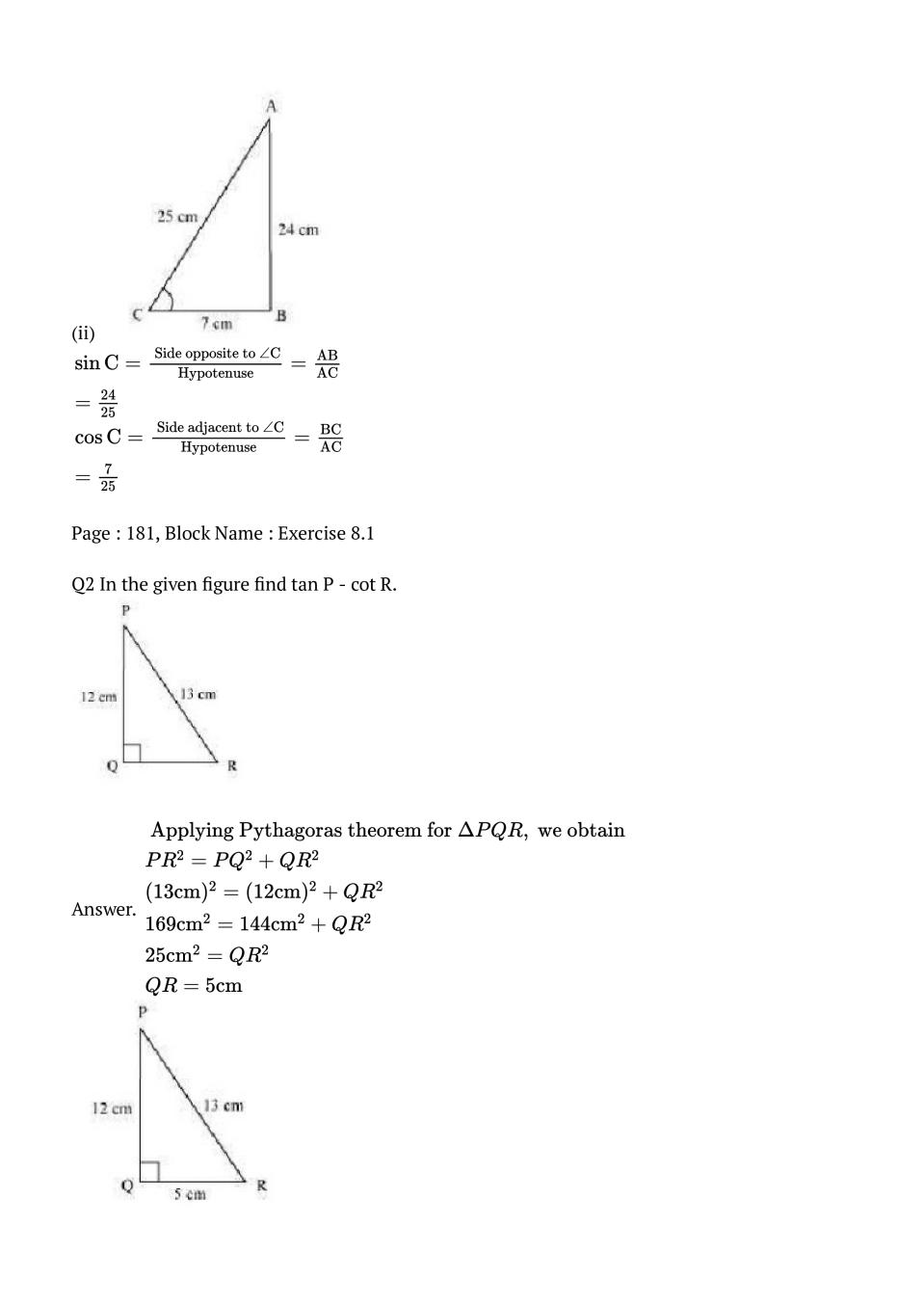
\(\begin{array}{l}{ \sin \mathrm{C}=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle \mathrm{C}}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{\mathrm{AC}}} \\ {=\frac{24}{25}}\end{array}\) \(\begin{array}{l}{\cos \mathrm{C}=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle \mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{Hypotenuse}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{AC}}} \\ {=\frac{7}{25}}\end{array}\)
Q.2: In the given figure find tan P - cot R.
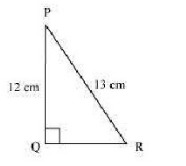
Ans : \(\begin{array}{l}{\text { Applying Pythagoras theorem for } \Delta P Q R, \text { we obtain }} \\ {P R^{2}=P Q^{2}+Q R^{2}} \\ {(13 \mathrm{cm})^{2}=(12 \mathrm{cm})^{2}+Q R^{2}} \\ {169 \mathrm{cm}^{2}=144 \mathrm{cm}^{2}+Q R^{2}} \\ {25 \mathrm{cm}^{2}=Q R^{2}} \\ {Q R=5 \mathrm{cm}}\end{array}\)\(\begin{aligned} \tan \mathbf{P} &=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle P}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle P}=\frac{Q R}{P Q} \\ &=\frac{5}{12} \\ \cot R &=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle R}{\text { Side opposite to } \angle R}=\frac{Q R}{P Q} \\ &=\frac{5}{12} \end{aligned}\) \(\tan \mathrm{P}-\cot \mathrm{R}=\frac{5}{12}-\frac{5}{12}=0\)
Q.3: If \(\sin A=\frac{3}{4}, \text { calculate cos } A \text { and } \tan A.\)
Ans : Let\(\Delta A B C \text { be a right-angled triangle, right-angled at point } B\)Given that, \(\begin{array}{l}{\sin A=\frac{3}{4}} \\ {\frac{B C}{A C}=\frac{3}{4}}\end{array}\) Let BC be 3k . Therefore, AC will be 4k , where k is a positive integer. Applying Pythagoras theorem in \(\triangle ABC \), we obtain \(\begin{array}{l}{A C^{2}=A B^{2}+B C^{2}} \\ {(4 k)^{2}=A B^{2}+(3 k)^{2}} \\ {16 k^{2}-9 k^{2}=A B^{2}} \\ {7 k^{2}=A B^{2}} \\ {A B=\sqrt{7} k}\end{array}\) \(\begin{aligned} \cos A &=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A}{\text { Hypotent } t 0 \angle A} \\ &=\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{\sqrt{7 k}}{4 k}=\frac{\sqrt{7}}{4} \\ \tan A &=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle A}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A} \\ &=\frac{B C}{A B}=\frac{3 k}{\sqrt{7} k}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{7}} \end{aligned}\)
Q.4: Given \(15 \cot A=8 . \text { Find } \sin A \text { and } \sec A.\)
Ans : Consider a right-angled triangle, right-angled at B.Given that, \(\begin{array}{l}{\sin A=\frac{3}{4}} \\ {\frac{B C}{A C}=\frac{3}{4}}\end{array}\) Let BC be 3k. Therefore, AC will be 4k, where k is a positive integer. Applying Pythagoras theorem in \(\triangle \mathrm{ABC}\) , we obtain \(\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{AC}^{2}=\mathrm{AB}^{2}+\mathrm{BC}^{2}} \\ {(4 k)^{2}=\mathrm{AB}^{2}+(3 \mathrm{k})^{2}} \\ {16 \mathrm{k}^{2}-\mathrm{gk}^{2}=\mathrm{AB}^{2}} \\ {7 k^{2}=\mathrm{AB}^{2}} \\ {\mathrm{AB}=\sqrt{7} k}\end{array}\) \(\begin{aligned} \cos A &=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A}{\text { Hypotenuse }} \\ &=\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{\sqrt{7 k}}{4 k}=\frac{\sqrt{7}}{4} \end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned} \tan A &=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle A}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A} \\ &=\frac{B C}{A B}=\frac{3 k}{\sqrt{7} k}=\frac{3}{\sqrt{7}} \end{aligned}\) \(\begin{aligned} \cot A &=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A}{\text { Side opposite to } \angle A} \\ &=\frac{A B}{B C} \end{aligned}\) \(\begin{array}{c}{\text { It is given that, }} \\ {\text { cot } A=\frac{8}{15}} \\ {\frac{A B}{B C}=\frac{8}{15}}\end{array}\) Let AB be 8k.Therefore, 3C will be 15k, where k is a positive integer. Applying Pythagoras theorem in \(\triangle\)ABC, we obtain \(\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{AC}^{2}=\mathrm{AB}^{2}+\mathrm{BC}^{2}} \\ {=(8 k)^{2}+(15 k)^{2}} \\ {=64 k^{2}+225 \mathrm{k}^{2}} \\ {=289 \mathrm{k}^{2}} \\ {\mathrm{AC}=17 k}\end{array}\) \(\begin{aligned} \sin A &=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle A}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{B C}{A C} \\ &=\frac{15 k}{17 k}=\frac{15}{17} \\ \sec A &=\frac{\text { Hypotenuse }}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle A} \\ &=\frac{A C}{A B}=\frac{17}{8} \end{aligned}\)
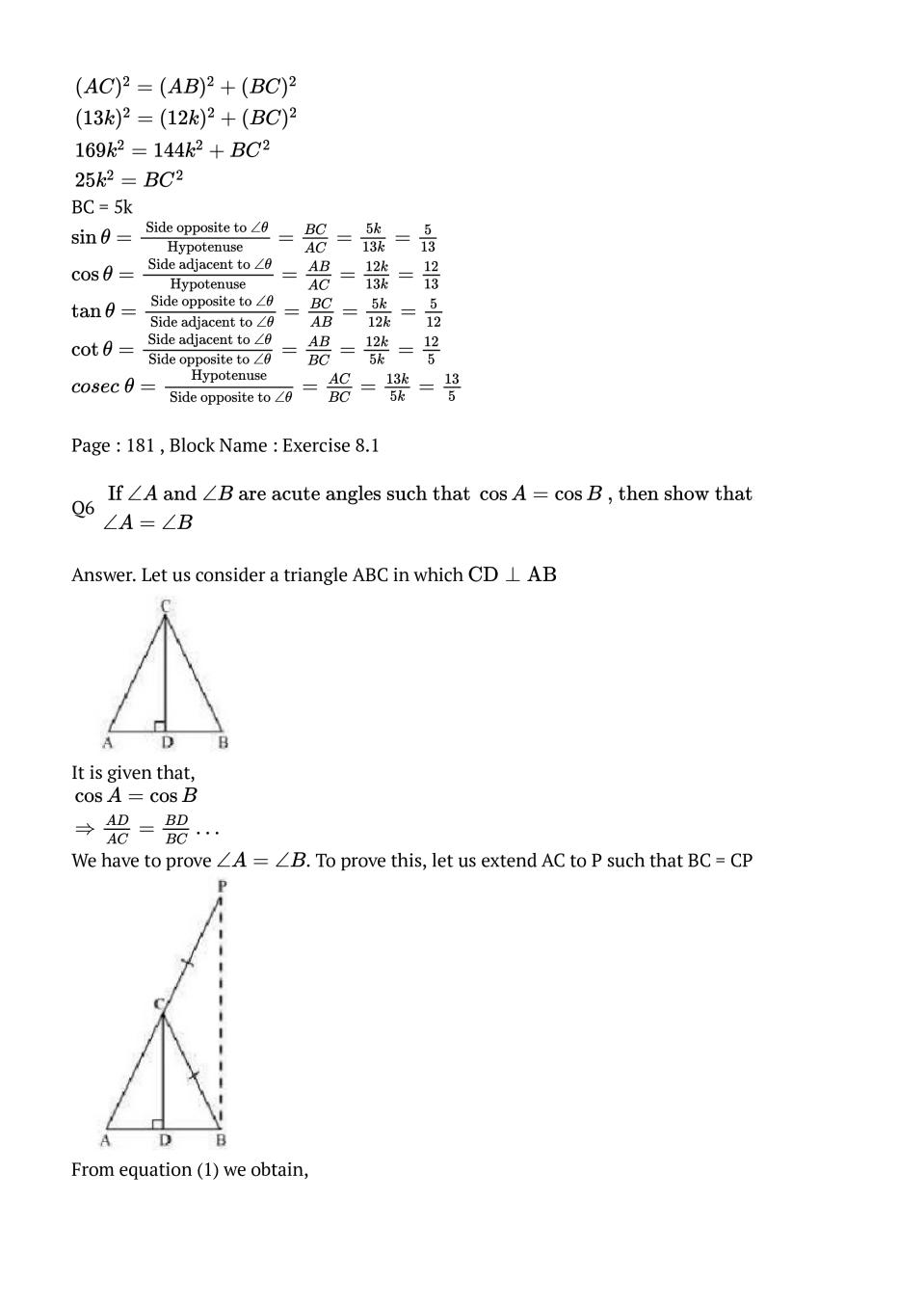
Q.5: Given \(\sec \theta=\frac{13}{12},\) calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
Ans : Consider a right-angle \(\triangle \mathrm{ABC}, \text { right-angled at point } \mathrm{B}\)\(\begin{array}{l}{\sec \theta=\frac{\text { Hypotenuse }}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle \theta}} \\ {\frac{13}{12}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{AB}}}\end{array}\) If AC is 13k, AB will be 12k, where k is a positive integer. Applying Pythagoras theorem in AABC, we obtain \(\begin{array}{l}{(A C)^{2}=(A B)^{2}+(B C)^{2}} \\ {(13 k)^{2}=(12 k)^{2}+(B C)^{2}} \\ {169 k^{2}=144 k^{2}+B C^{2}} \\ {25 k^{2}=B C^{2}}\end{array}\) BC = 5k \(\sin \theta=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle \theta}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{B C}{A C}=\frac{5 k}{13 k}=\frac{5}{13}\) \(\cos \theta=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle \theta}{\text { Hypotenuse }}=\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{12 k}{13 k}=\frac{12}{13}\) \(\tan \theta=\frac{\text { Side opposite to } \angle \theta}{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle \theta}=\frac{B C}{A B}=\frac{5 k}{12 k}=\frac{5}{12}\) \(\cot \theta=\frac{\text { Side adjacent to } \angle \theta}{\text { Side opposite to } \angle \theta}=\frac{A B}{B C}=\frac{12 k}{5 k}=\frac{12}{5}\) \(cosec \ \theta=\frac{\text { Hypotenuse }}{\text { Side opposite to } \angle \theta}=\frac{A C}{B C}=\frac{13 k}{5 k}=\frac{13}{5}\)
NCERT / CBSE Book for Class 10 Maths
You can download the NCERT Book for Class 10 Maths in PDF format for free. Otherwise you can also buy it easily online.
- Click here for NCERT Book for Class 10 Maths
- Click here to buy NCERT Book for Class 10 Maths
All NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit
All NCERT Solutions
You can also check out NCERT Solutions of other classes here. Click on the class number below to go to relevant NCERT Solutions of Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12.
| Class 4 | Class 5 | Class 6 |
| Class 7 | Class 8 | Class 9 |
| Class 10 | Class 11 | Class 12 |
Download the NCERT Solutions app for quick access to NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry. It will help you stay updated with relevant study material to help you top your class!
The post NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry appeared first on AglaSem Schools.
from AglaSem Schools https://ift.tt/2PypQiz
https://ift.tt/3dZyUWY https://ift.tt/3dZyUWY
























إرسال تعليق