NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science (Indian Constitution) Chapter 10 the Philosophy of the Constitution– Here are all the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Political Science (Indian Constitution) Chapter 10. This solution contains questions, answers, images, explanations of the complete chapter 10 titled Of the Philosophy of the Constitution taught in Class 11. If you are a student of Class 11 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Political Science (Indian Constitution), then you must come across chapter 10 the Philosophy of the Constitution After you have studied lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science (Indian Constitution) Chapter 10 the Philosophy of the Constitution in one place.
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science Chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution
Here on AglaSem Schools, you can access to NCERT Book Solutions in free pdf for Political Science for Class 11 so that you can refer them as and when required. The NCERT Solutions to the questions after every unit of NCERT textbooks aimed at helping students solving difficult questions.
For a better understanding of this chapter, you should also see summary of Chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution , Political Science, Class 11.
| Class | 11 |
| Subject | Political Science |
| Book | India Constitution At Work |
| Chapter Number | 10 |
| Chapter Name |
The Philosophy of the Constitution |
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution
Class 11, Political Science chapter 10, The Philosophy of the Constitution solutions are given below in PDF format. You can view them online or download PDF file for future use.
The Philosophy of the Constitution
Did you find NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution helpful? If yes, please comment below. Also please like, and share it with your friends!
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution- Video
You can also watch the video solutions of NCERT Class11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution here.
Video – will be available soon.
If you liked the video, please subscribe to our YouTube channel so that you can get more such interesting and useful study resources.
Download NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution In PDF Format
You can also download here the NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution in PDF format.
Click Here to download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution
Question & Answer
Q.1: The following are certain laws. Are they connected with any value? If yes, then what is the underlying value? Give reasons.
(a) Both daughters and sons will have share in the family property.
(b) There will be different slabs of sales tax on different consumer items.
(c) Religious instructions will not be given in any government school.
(d) There shall be no begar or forced labour
Ans : (a) Idea of equality and social justice. It treats both children equally by giving inheritance to them irrespective of their gender. (b) Economic justice as it reflects the importance of certain consumer items for people and seeks to discourage the consumption of other items deemed as non-essential. (c) Secularism as it shows that the government does not give importance to any religion in particular. (d) Idea of social justice as it strives to end forced labour and protect workers from exploitation.
Q.2: Which of the options given below cannot be used to complete the following statement?Democratic countries need a constitution to Check the power of the government. Protect minorities from majority. Bring independence from colonial rule.
Ensure that a long-term vision is not lost by momentary passions. Bring social change in peaceful manner.
Ans : (iii) Bring independence from colonial rule.
Q.3: The following are different positions about reading and understanding Constituent Assembly debates.
(i) Which of these statements argues that Constituent Assembly debates are relevant even today? Which statement says that they are not relevant?
(ii) With which of these positions do you agree and why?
(a) Common people are too busy in earning livelihood and meeting different pressures of life. They can’t understand the legal language of these debates.
(b) The conditions and challenges today are different from the time when the Constitution was made. To read the ideas of Constitution makers and use them for our new times is trying to bring past in the present
(c) Our ways of understanding the world and the present challenges have not changed totally. Constituent Assembly debates can provide us reasons why certain practises are
important. In a period when constitutional practises are being challenged, not knowing the reasons can destroy them.
Ans : (i) The statement that argues that Constituent Assembly debates are relevant event today is c. (c) Our ways of understanding the world and the present challenges have not changed totally. Constituent Assembly debates can provide us reasons why certain practises are important. In a period when constitutional practises are being challenged, not knowing the reasons can destroy them. The statement that argues that Constituent Assembly debates are not relevant today is b. (b) The conditions and challenges today are different from the time when the Constitution was made. To read the ideas of Constitution makers and use them for our new times is trying to bring past in the present (ii) (c) Our ways of understanding the world and the present challenges have not changed totally. Constituent Assembly debates can provide us reasons why certain practises are important. In a period when constitutional practises are being challenged, not knowing the reasons can destroy them. The statement above is correct because the values that are enshrined in the Constitution are universal in nature and constitute a safeguard for the rights of the citizens. It is necessary to uphold these values as they are relevant to society in all ages. The breakdown of Constitutional values would lead to chaos and endanger the rights of the citizens as well as the integrity of the country.
Q.4: Explain the difference between the Indian Constitution and western ideas in the light of
(a) Understanding of secularism.
(b) Articles 370 and 371.
(c) Affirmative action.
(d) Universal adult franchise.
Ans : (a) Indian secularism is based on principled distance whereas that of western secularism is based on mutual exclusion. In India, every religion is treated equally so that every citizen can be treated equally and can enjoy a life of dignity. In the west, religion cannot interfere in matters of State and the State cannot interfere in matters of religion. (b) The articles 370 and 371 give special rights to the state of Jammu and Kashmir and the north-eastern states respectively according to their peculiar social and historical background. This type of provision of accommodation is not found in western countries. (c) Affirmative action in India is based on principle of social justice without compromising on individual liberties. In India affirmative action was introduced two decades before it was introduced in US (d) Every Indian citizen whose age is 18 years or above, is eligible to vote whereas in established democratic countries right to vote was extended to women and working class in the 20th century after a long struggle.
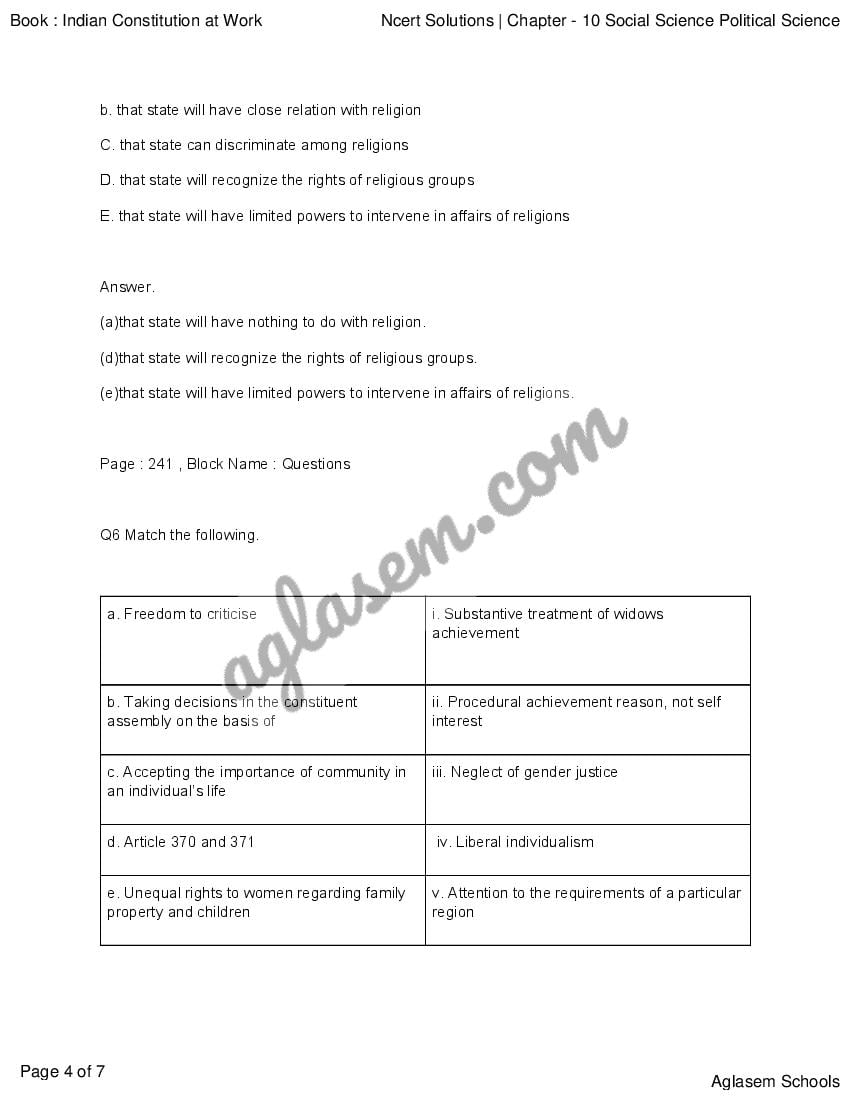
Q.5: Which of the following principles of secularism are adopted in the Constitution of India?
(a) that state will have nothing to do with religion
(b) that state will have close relation with religion
(c) that state can discriminate among religions
(d) that state will recognise rights of religious groups
(e) that state will have limited powers to intervene in affairs of religions
Ans : (d) that state will recognise rights of religious groups (e) that state will have limited powers to intervene in affairs of religions
NCERT / CBSE Book for Class 11 Political Science
You can download the NCERT Book for Class 11 Political Science in PDF format for free. Otherwise you can also buy it easily online.
- Click here for NCERT Book for Class 11 Political Science
- Click here to buy NCERT Book for Class 11 Political Science
All NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 History
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Geography
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Sociology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Statistics
All NCERT Solutions
You can also check out NCERT Solutions of other classes here. Click on the class number below to go to relevant NCERT Solutions of Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12.
| Class 4 | Class 5 | Class 6 |
| Class 7 | Class 8 | Class 9 |
| Class 10 | Class 11 | Class 12 |
Download the NCERT Solutions app for quick access to NCERT Solutions Class 11 Political Science Chapter 10 The Philosophy of the Constitution. It will help you stay updated with relevant study material to help you top your class!
The post NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science (Indian Constitution) Chapter 10 the Philosophy of the Constitution appeared first on AglaSem Schools.
from AglaSem Schools https://ift.tt/3aTXwi2
https://ift.tt/eA8V8J https://ift.tt/eA8V8J






إرسال تعليق