NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves – Here are all the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7. This solution contains questions, answers, images, explanations of the complete chapter 7 titled Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves of Accountancy taught in Class 11. If you are a student of Class 11 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Accountancy, then you must come across chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves. After you have studied lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves in one place.
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves
Here on AglaSem Schools, you can access to NCERT Book Solutions in free pdf for Accountancy for Class 11 so that you can refer them as and when required. The NCERT Solutions to the questions after every unit of NCERT textbooks aimed at helping students solving difficult questions.
For a better understanding of this chapter, you should also see summary of Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves , Accountancy, Class 11.
| Class | 11 |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Book | Financial Accounting Part 1 |
| Chapter Number | 7 |
| Chapter Name |
Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves |
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves
Class 11, Accountancy chapter 7, Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves solutions are given below in PDF format. You can view them online or download PDF file for future use.
Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves Download
Did you find NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves helpful? If yes, please comment below. Also please like, and share it with your friends!
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves- Video
You can also watch the video solutions of NCERT Class11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves here.
Video – will be available soon.
If you liked the video, please subscribe to our YouTube channel so that you can get more such interesting and useful study resources.
Download NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves In PDF Format
You can also download here the NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves in PDF format.
Click Here to download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves
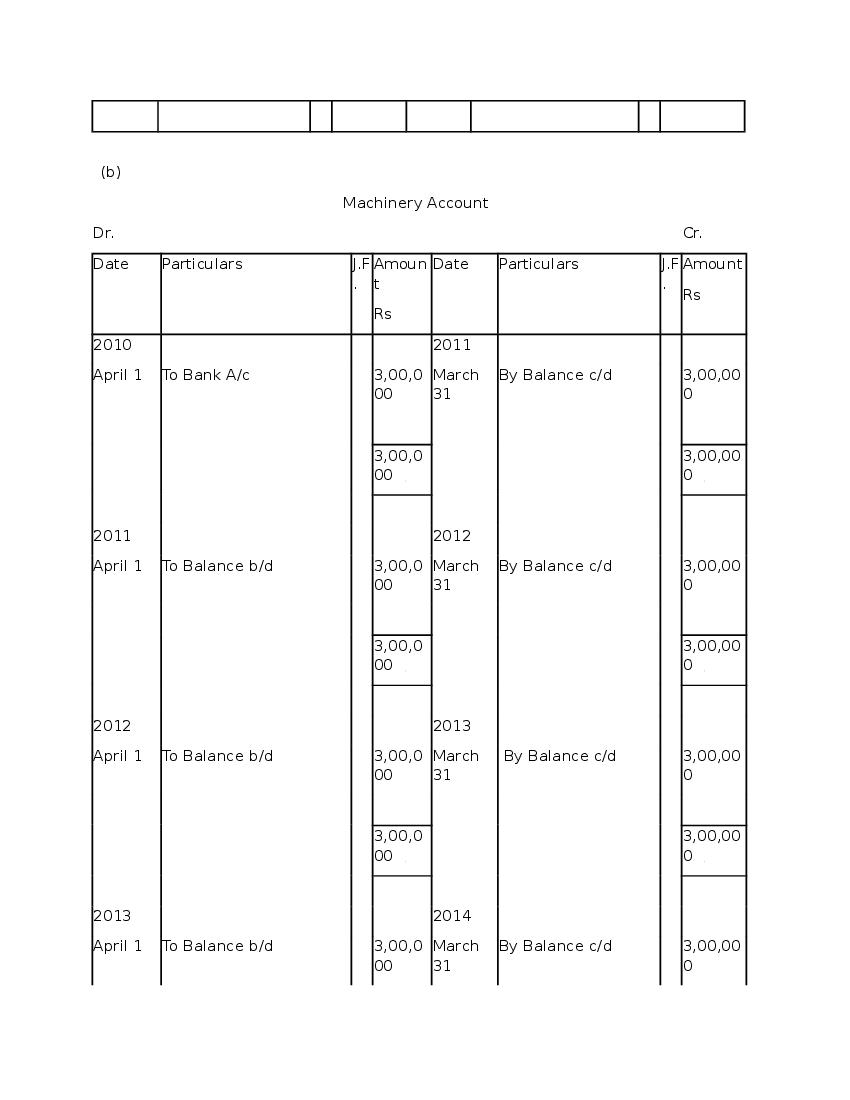
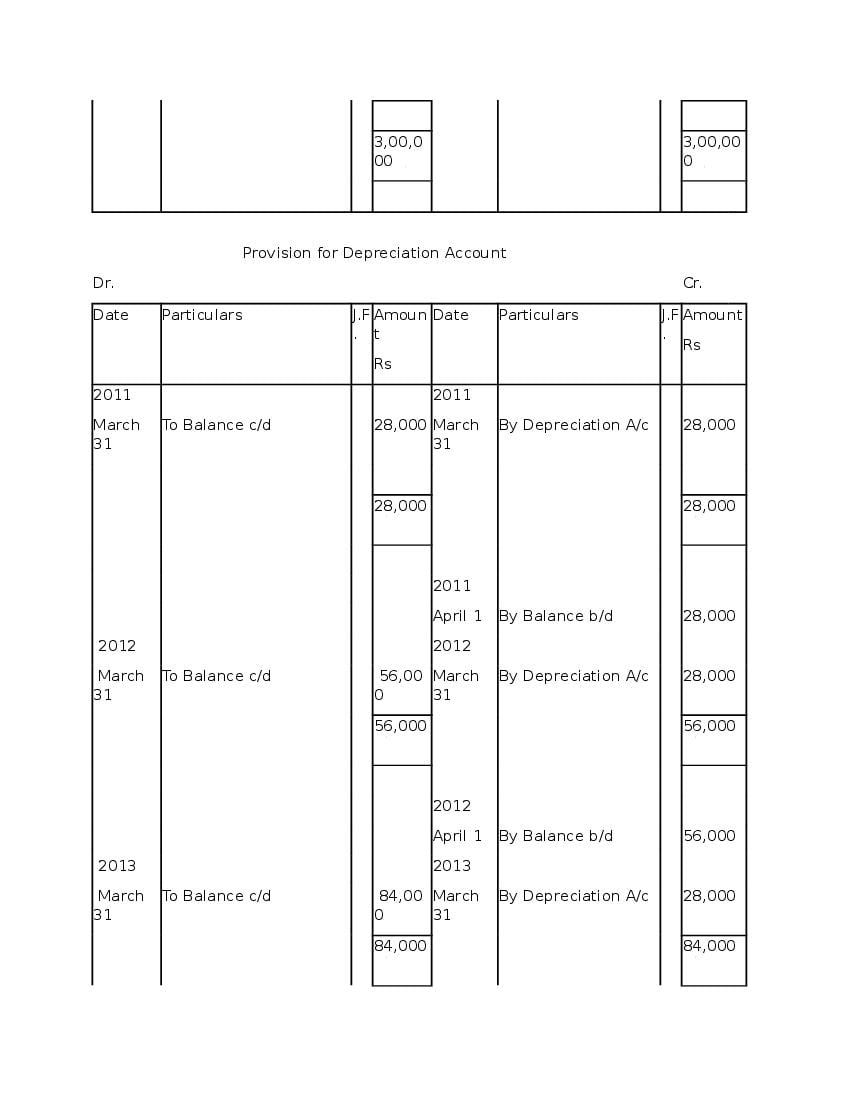
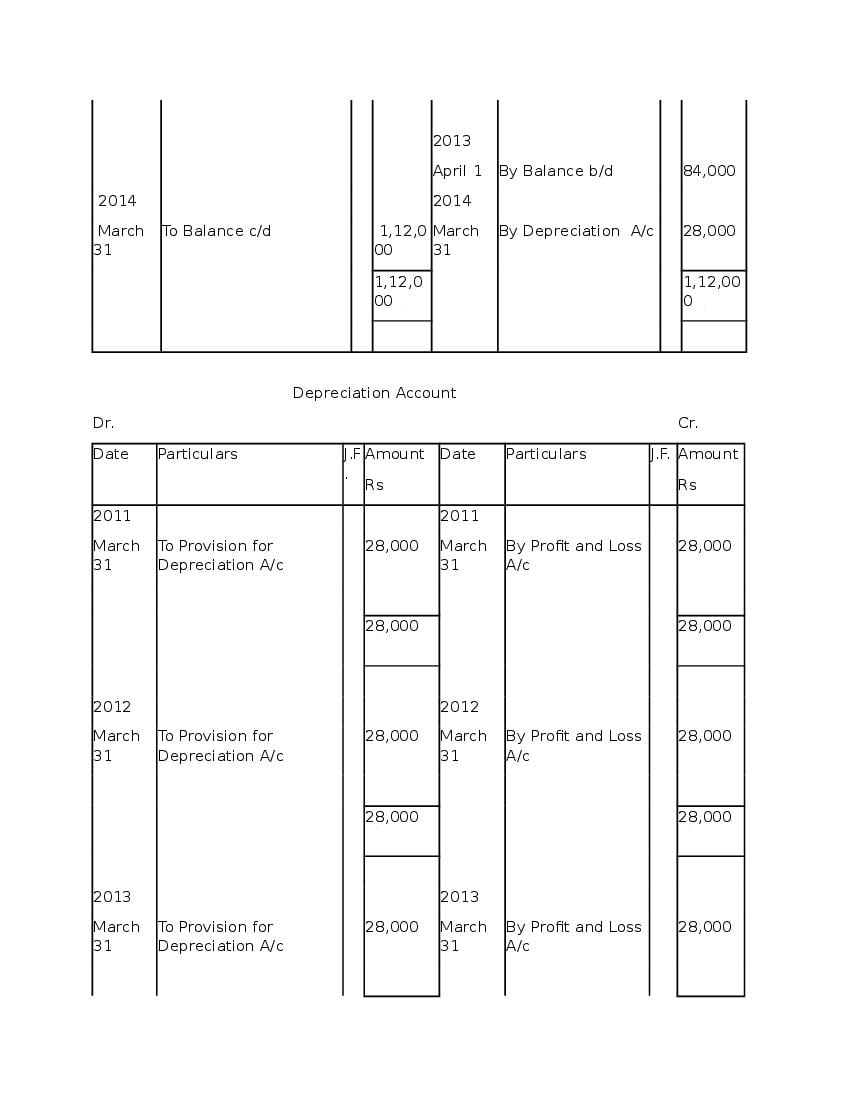
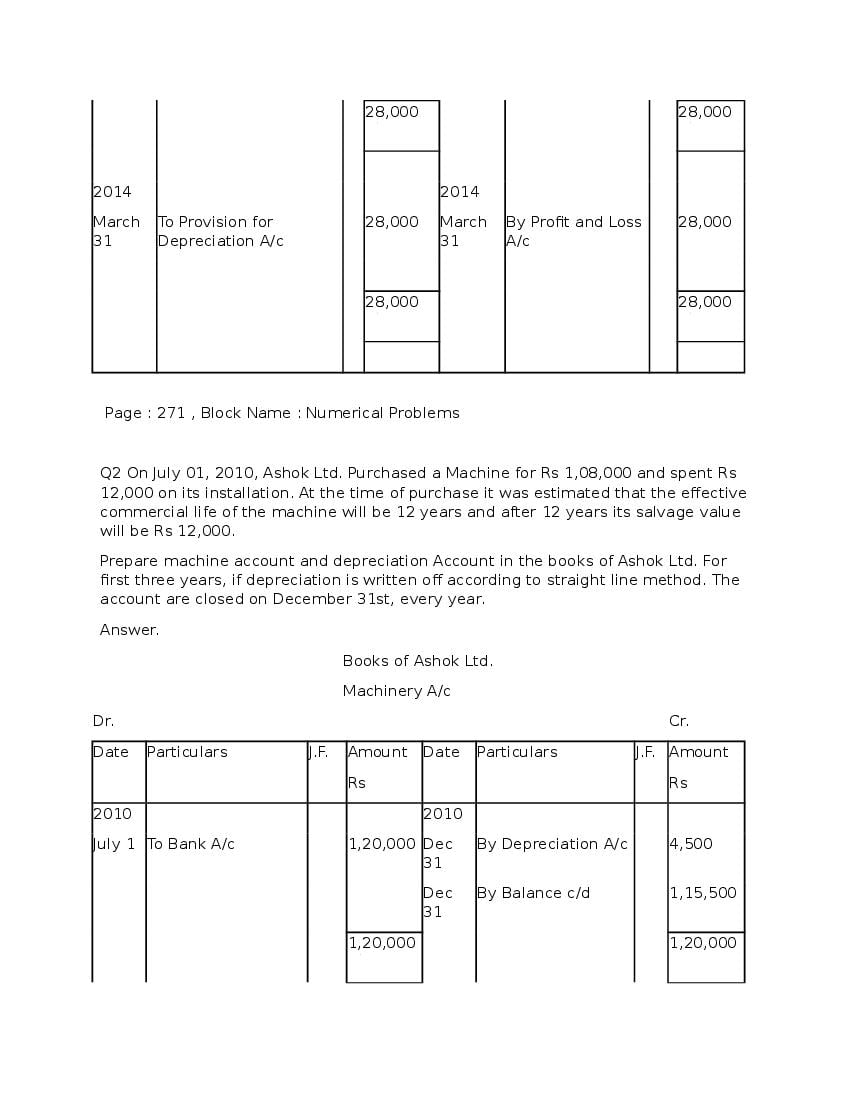
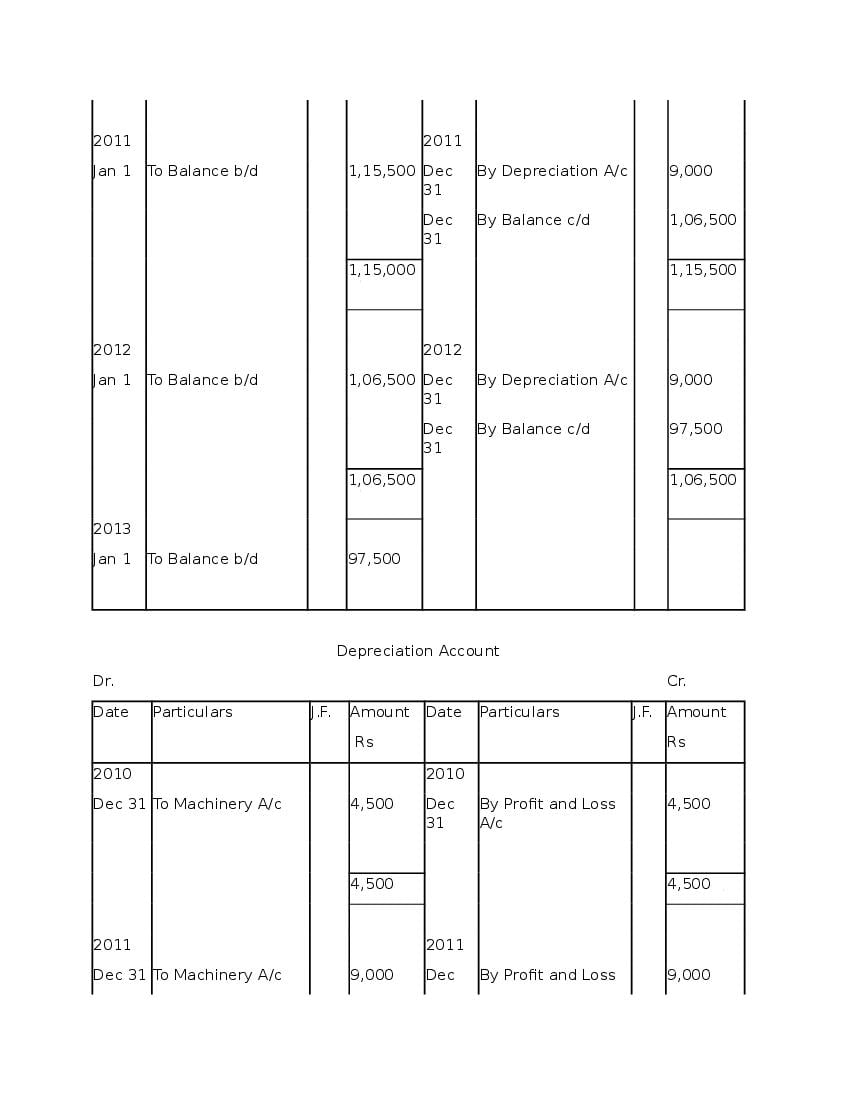
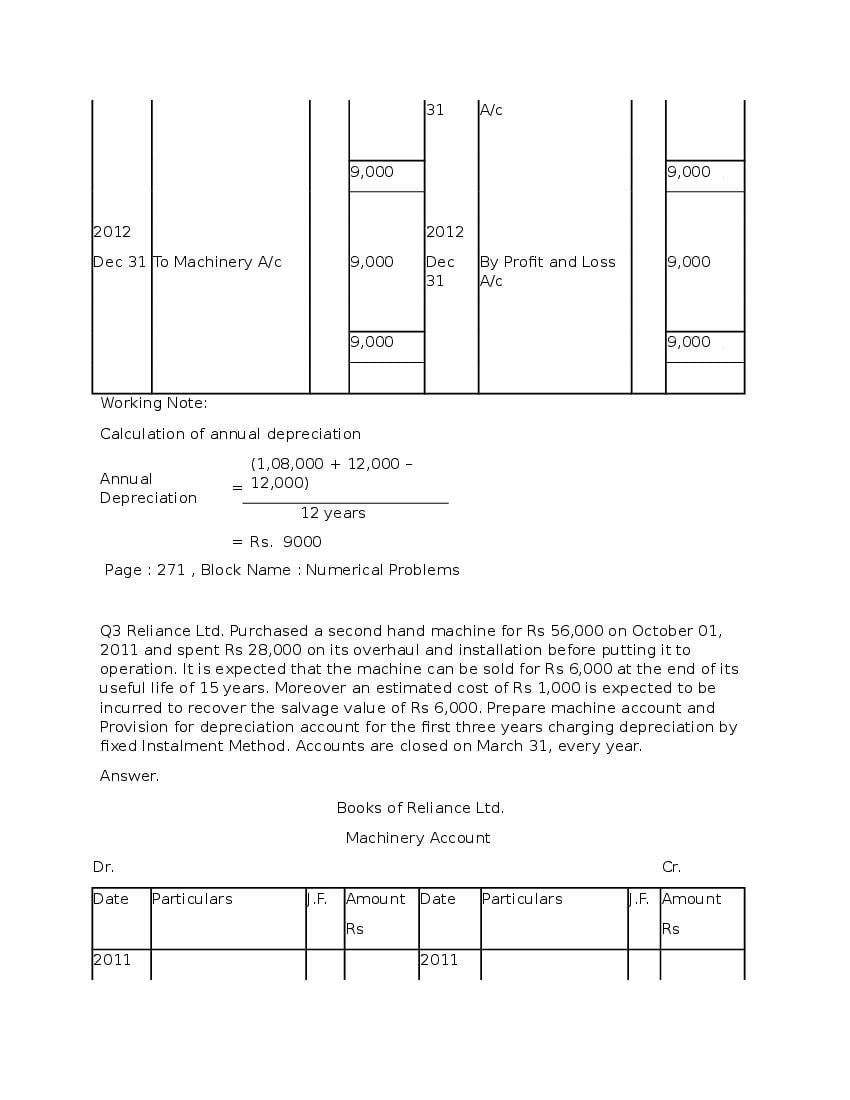
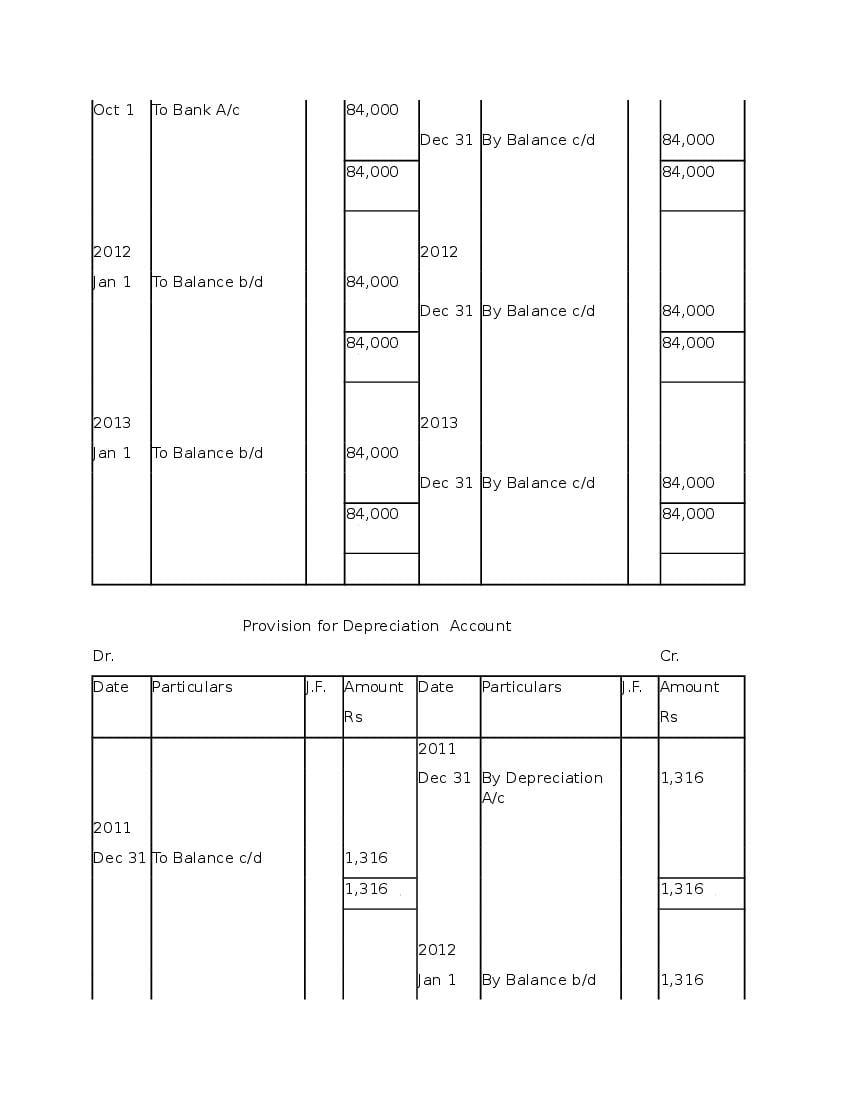
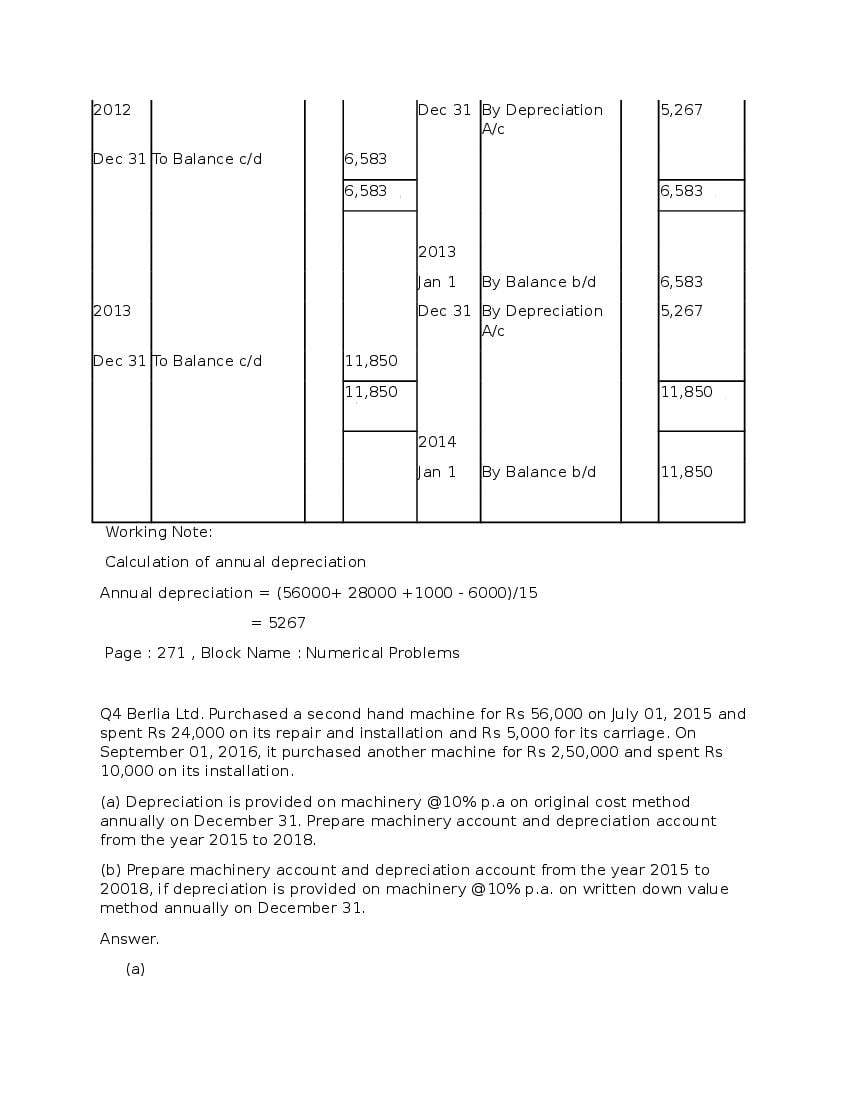
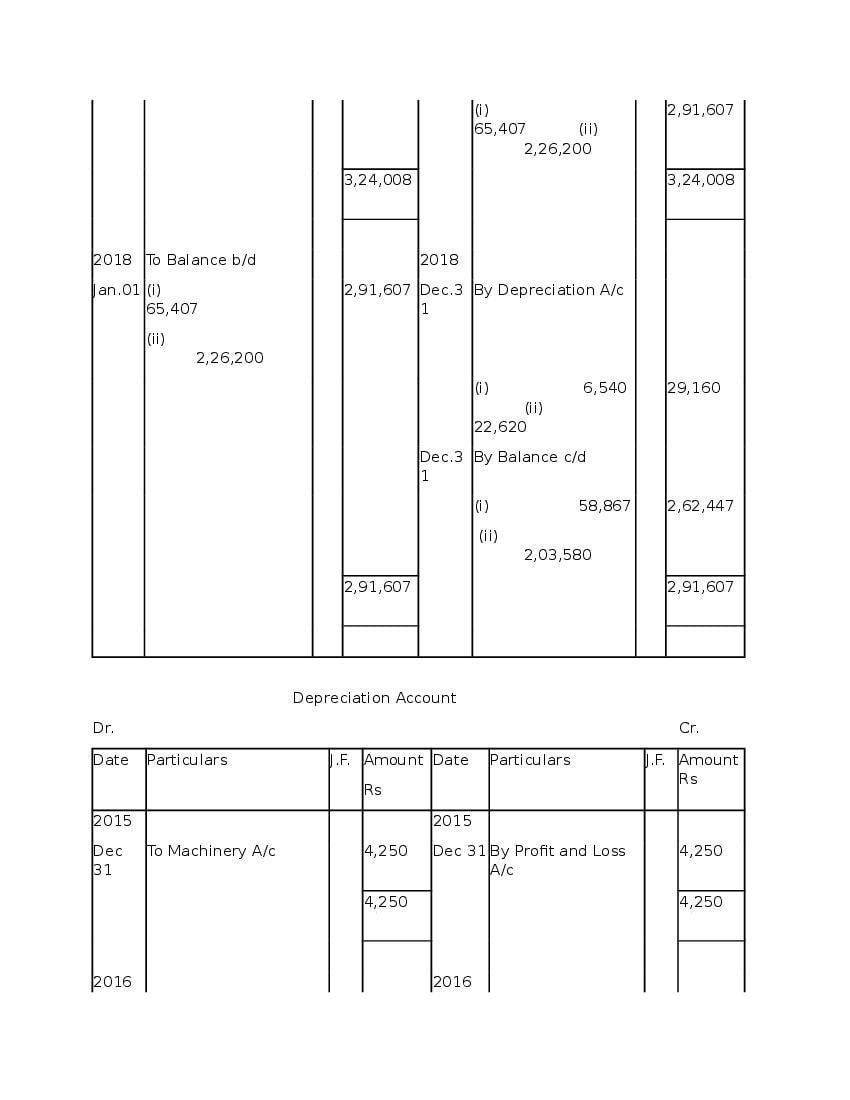
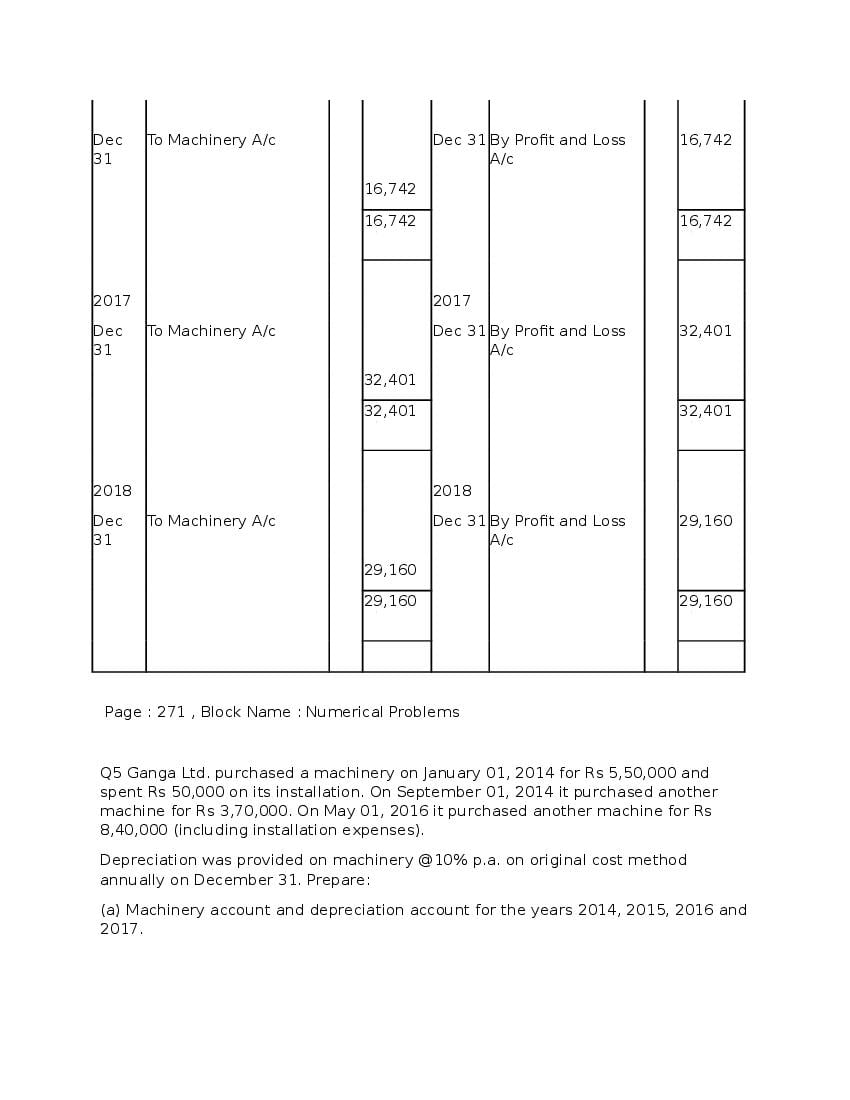
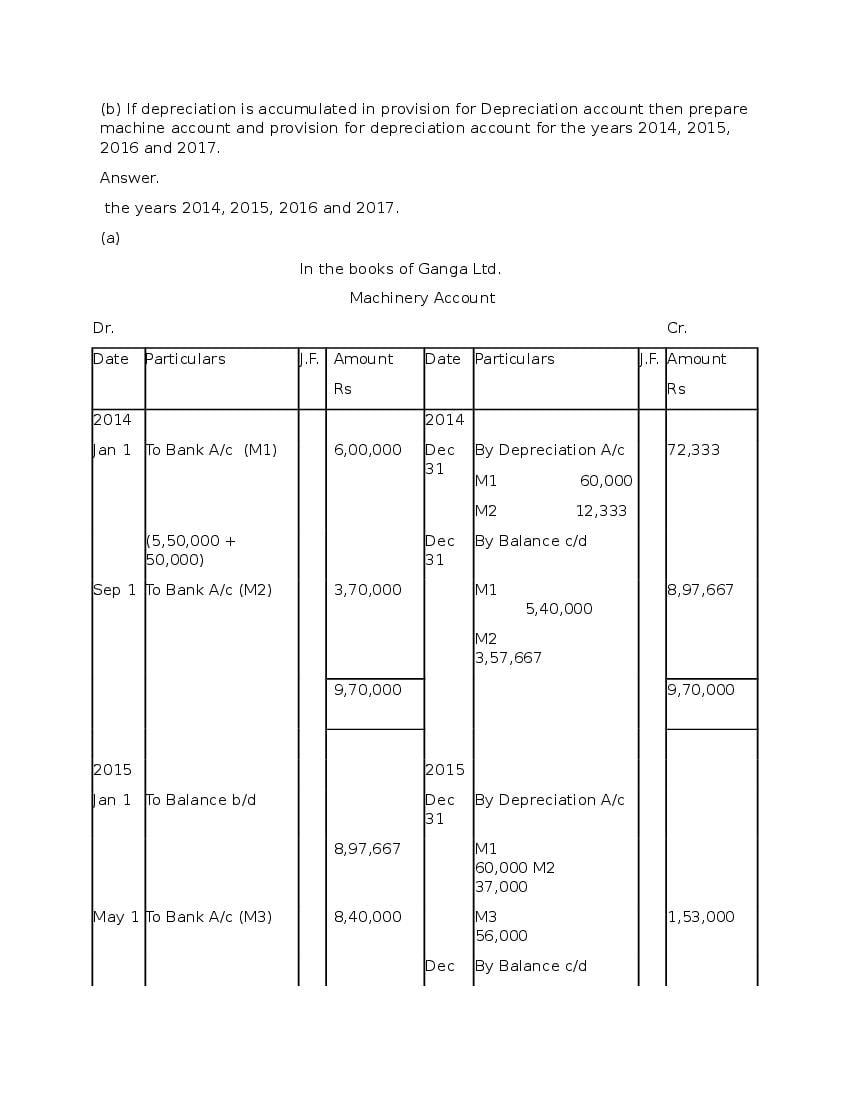
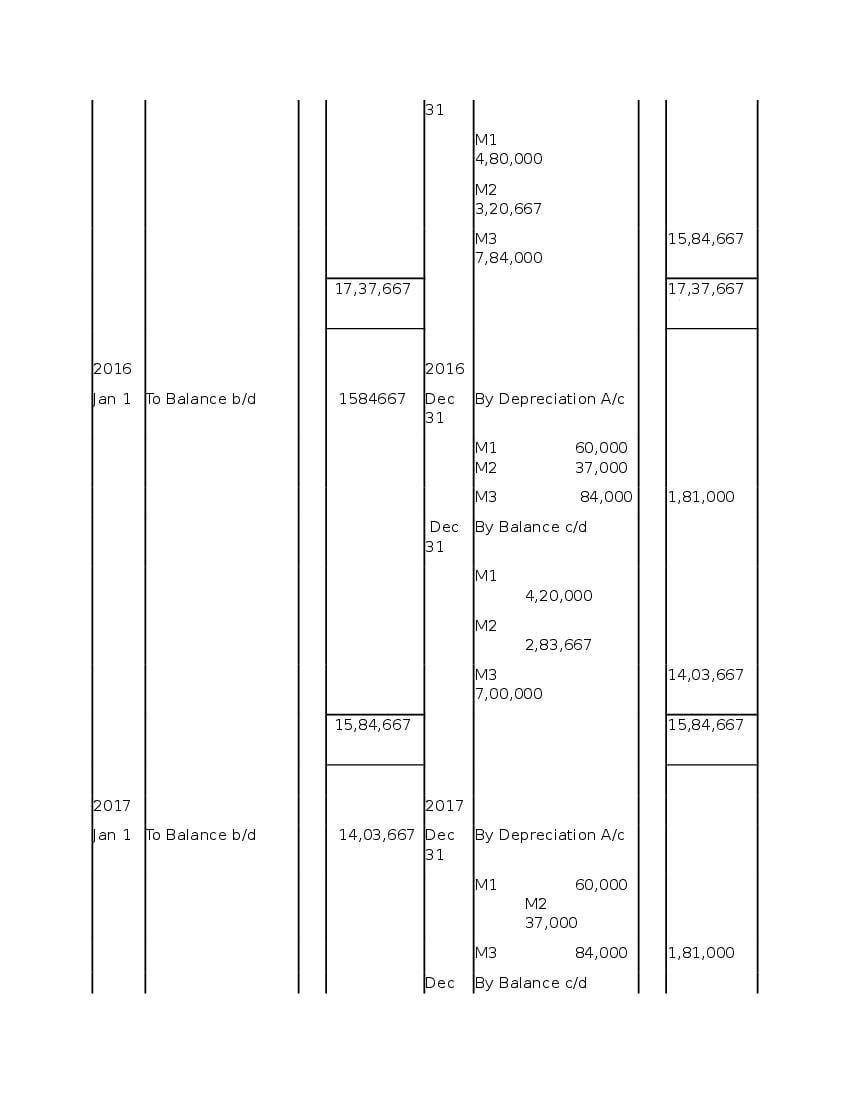
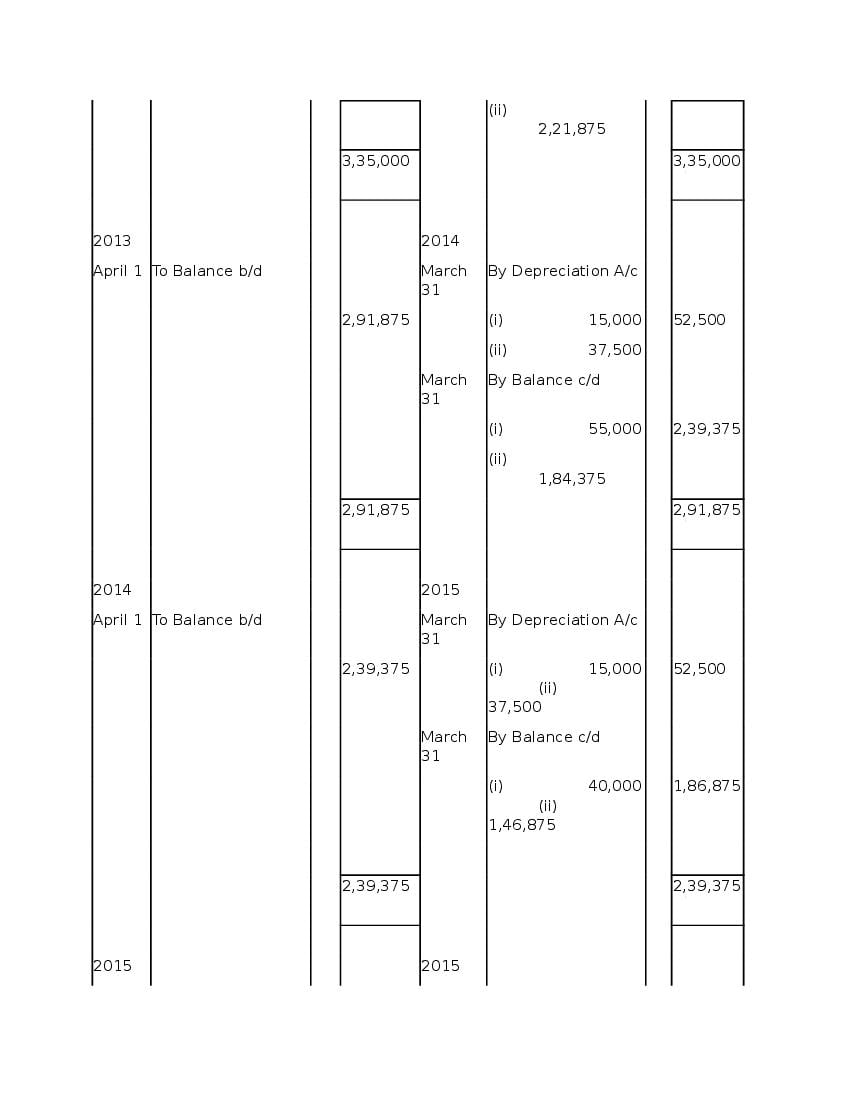
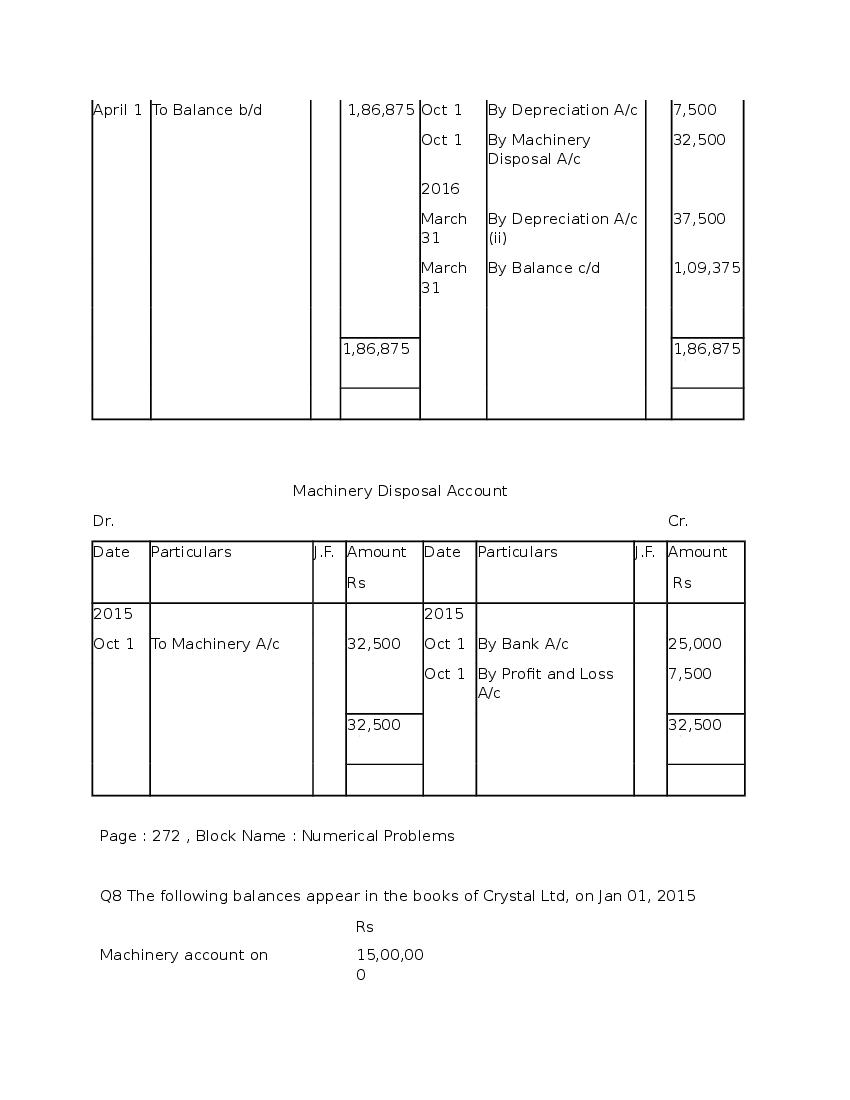
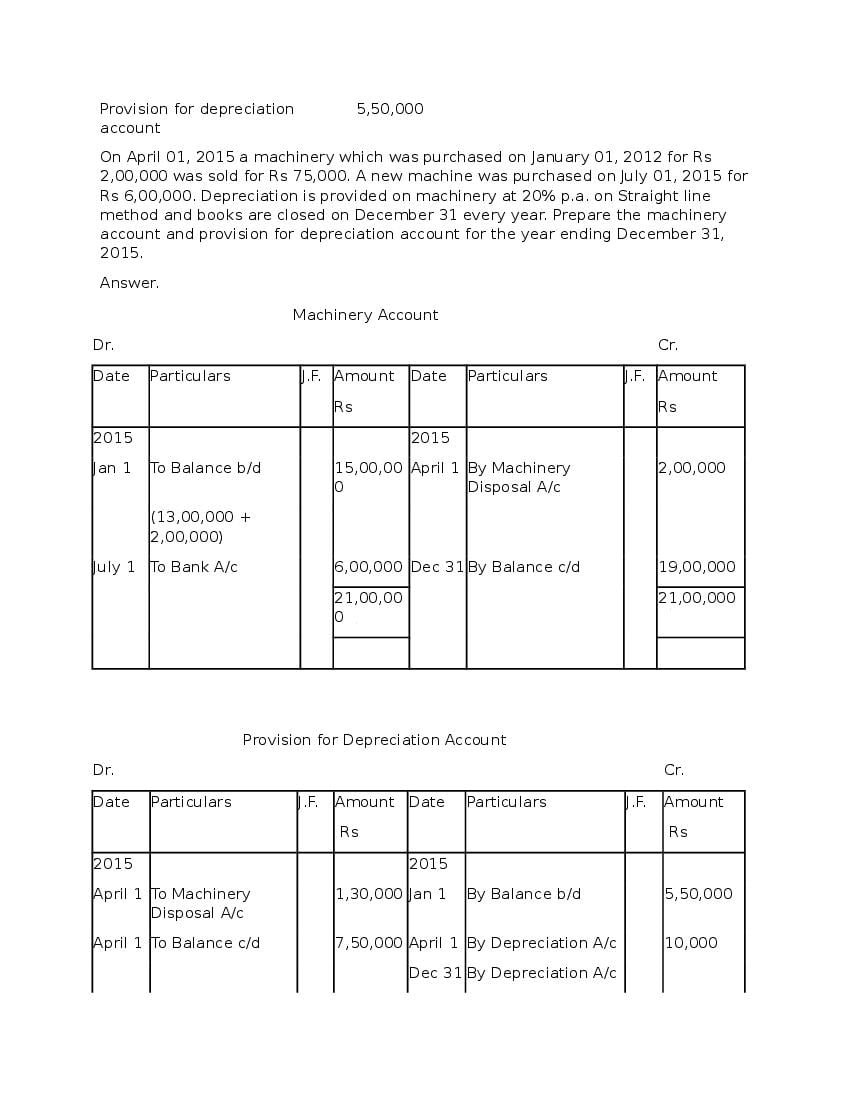
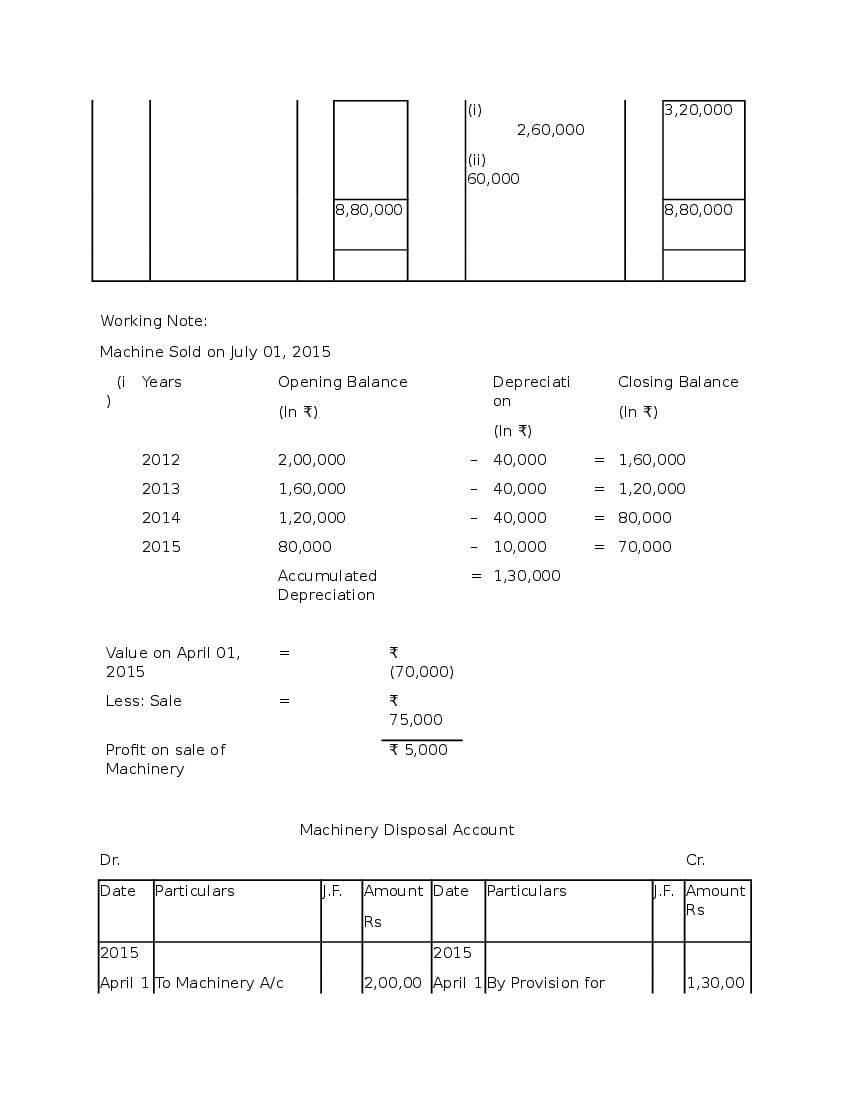
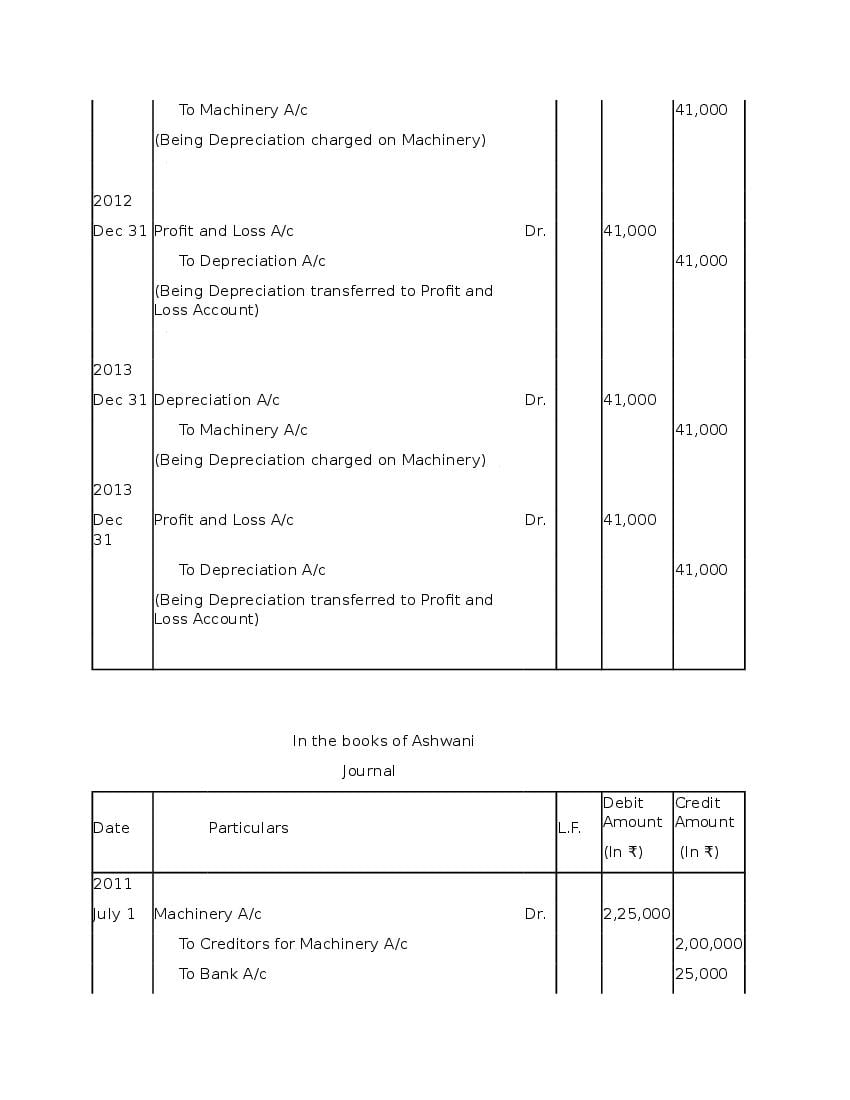
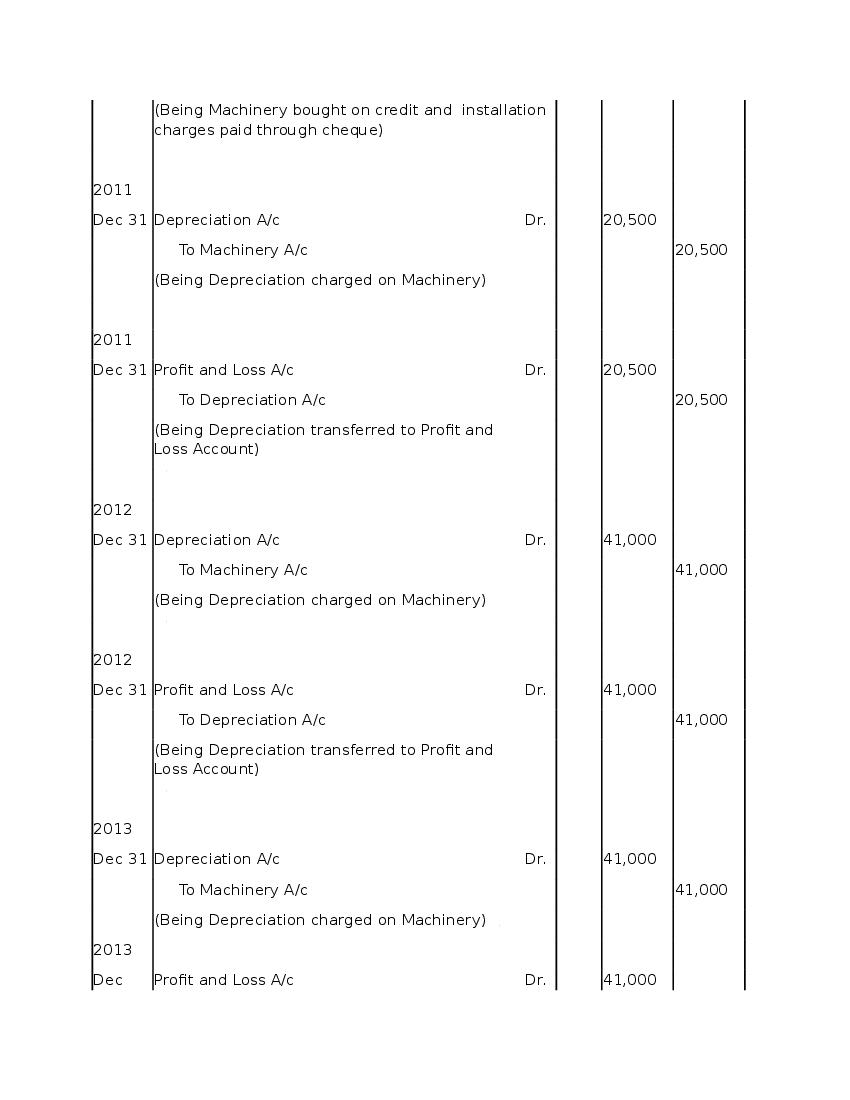
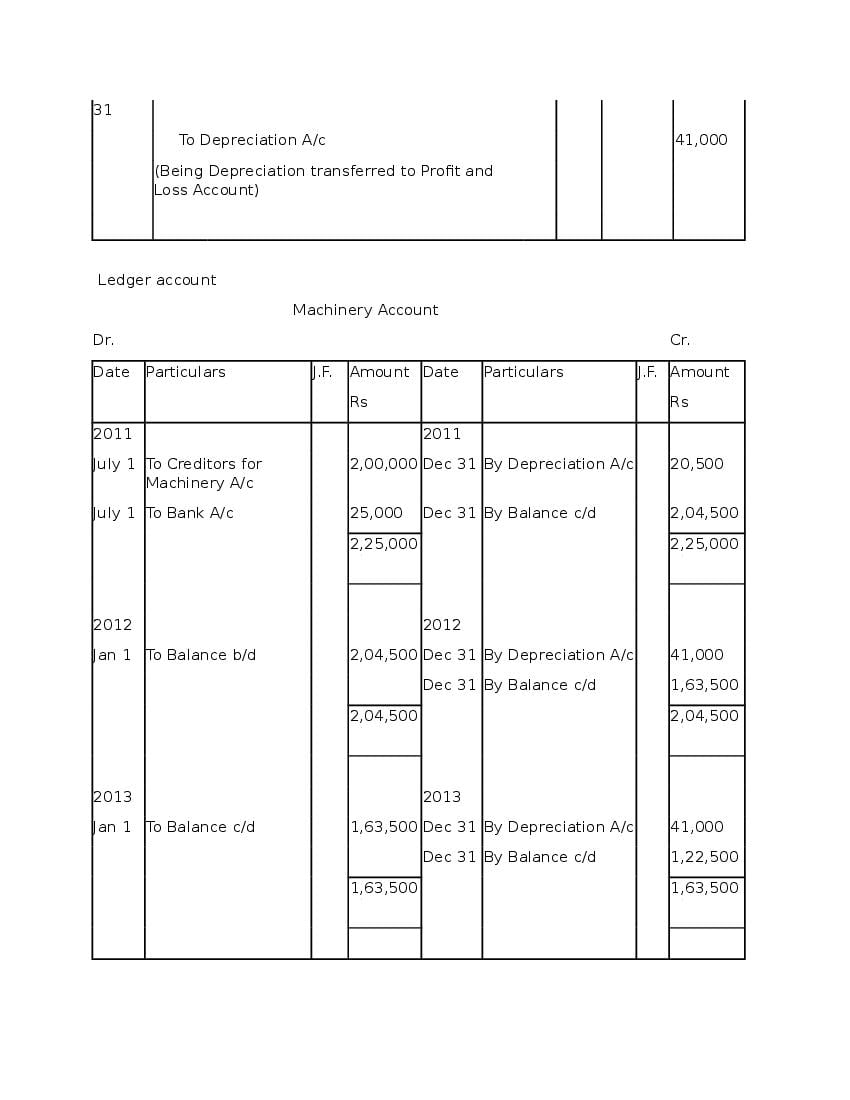
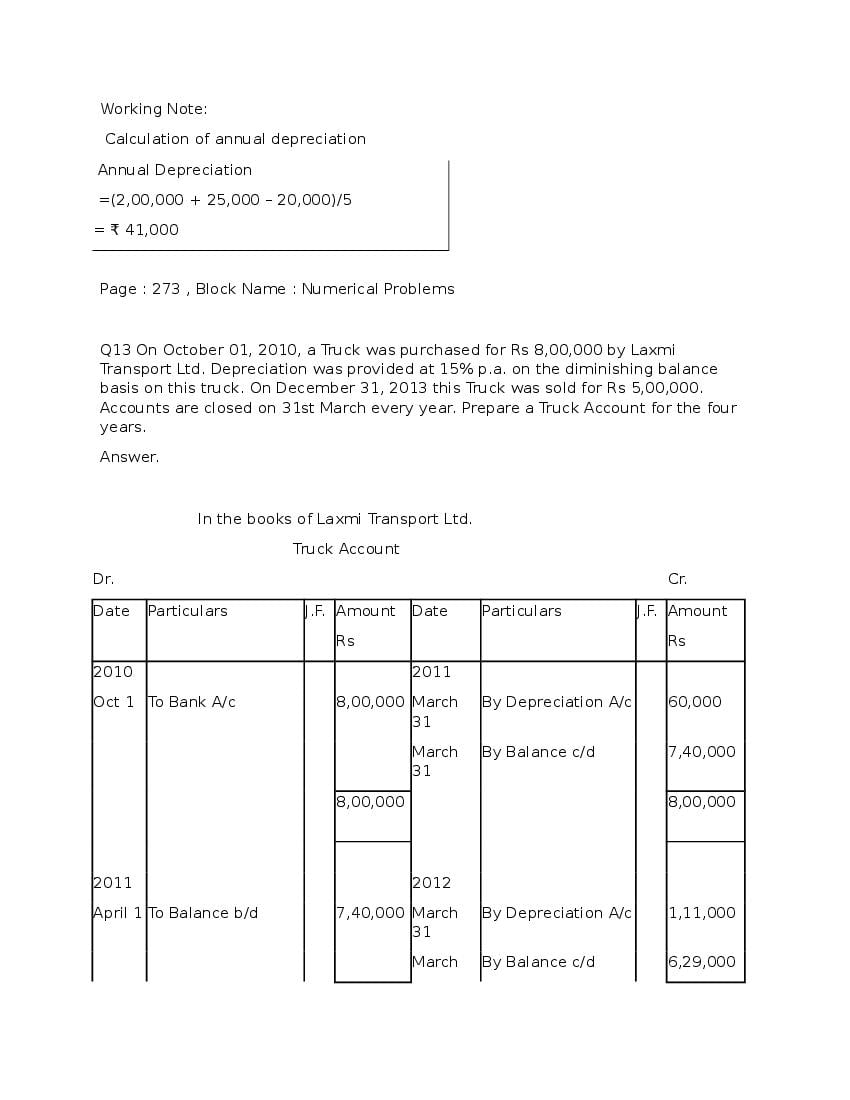
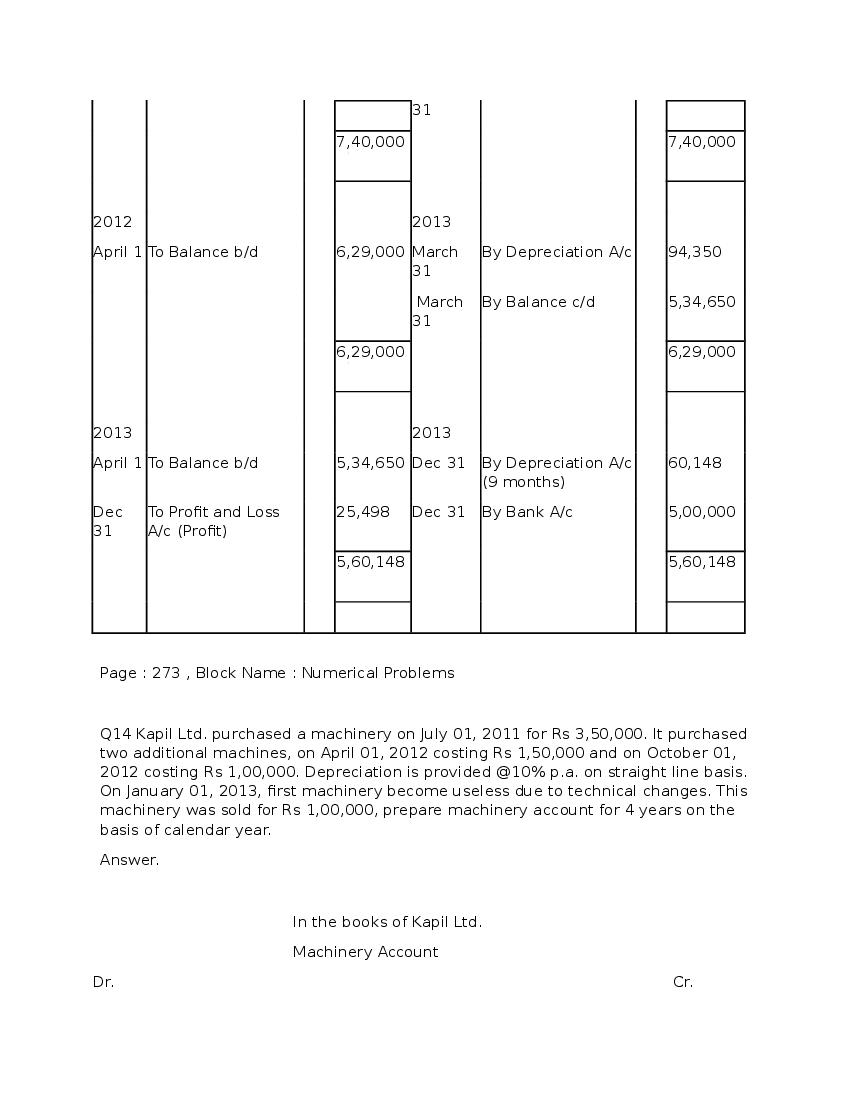
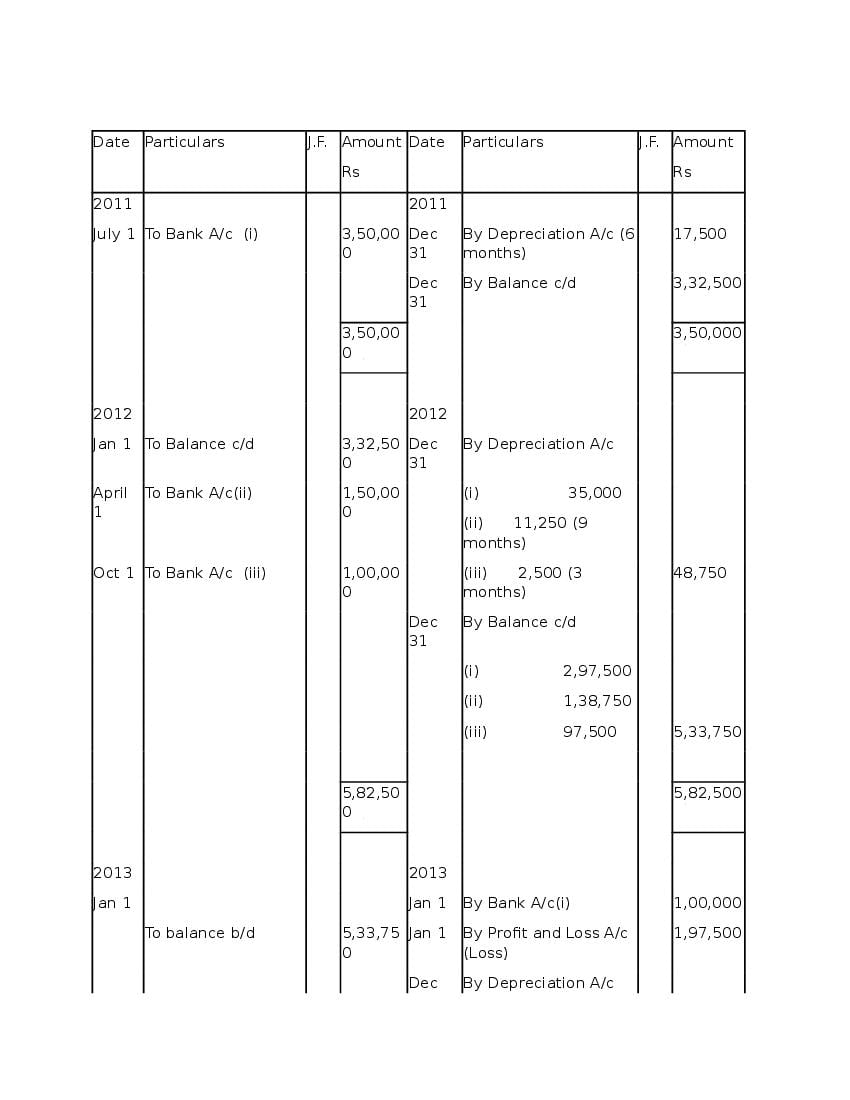
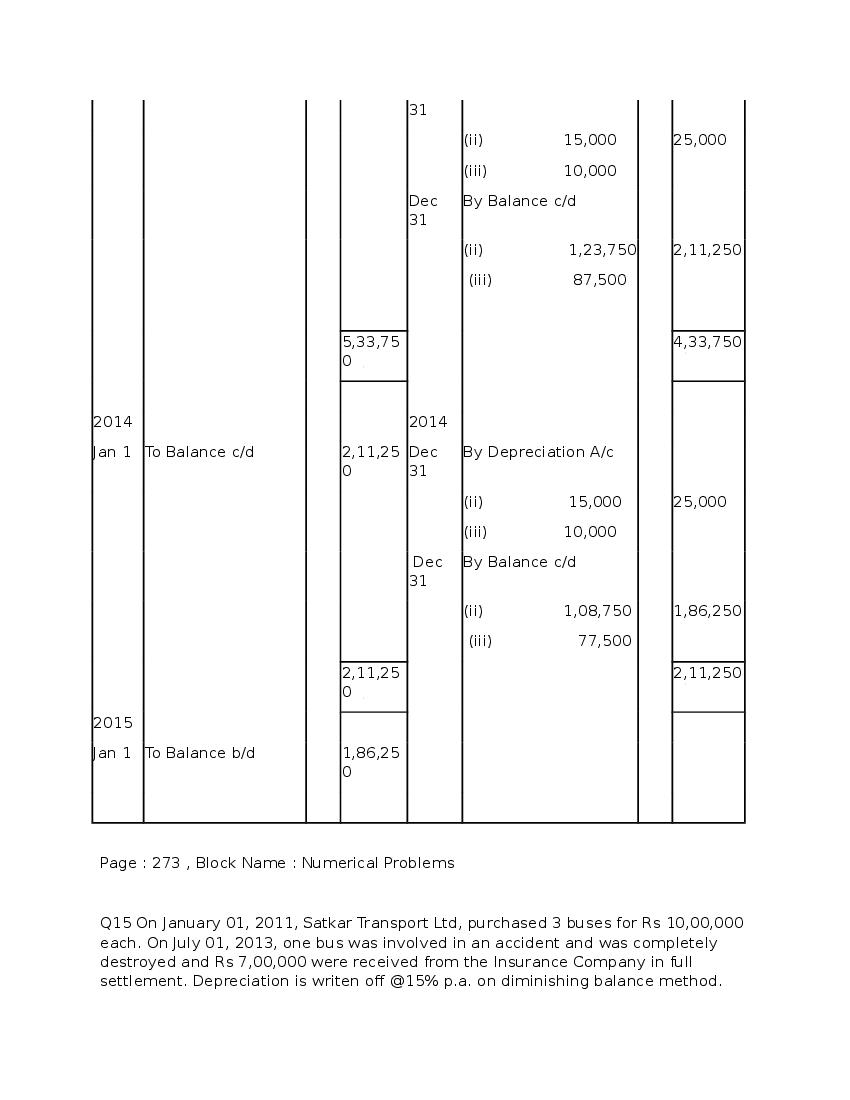
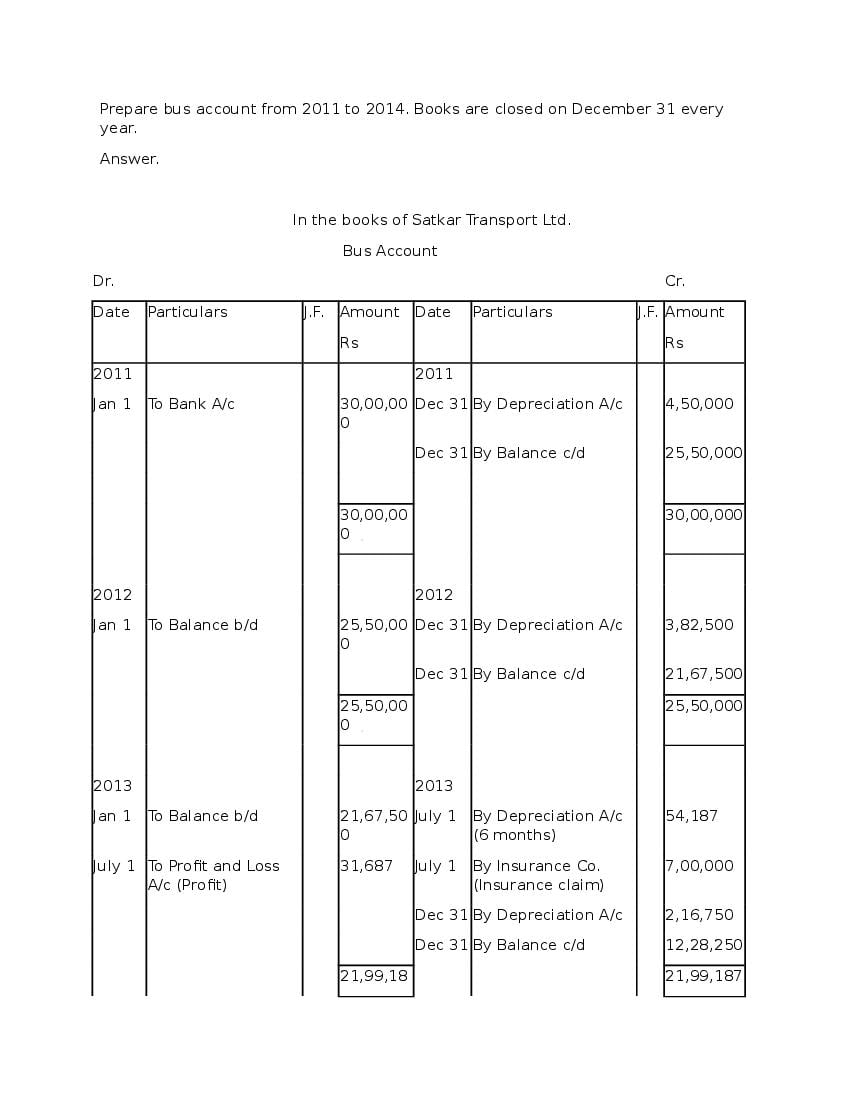
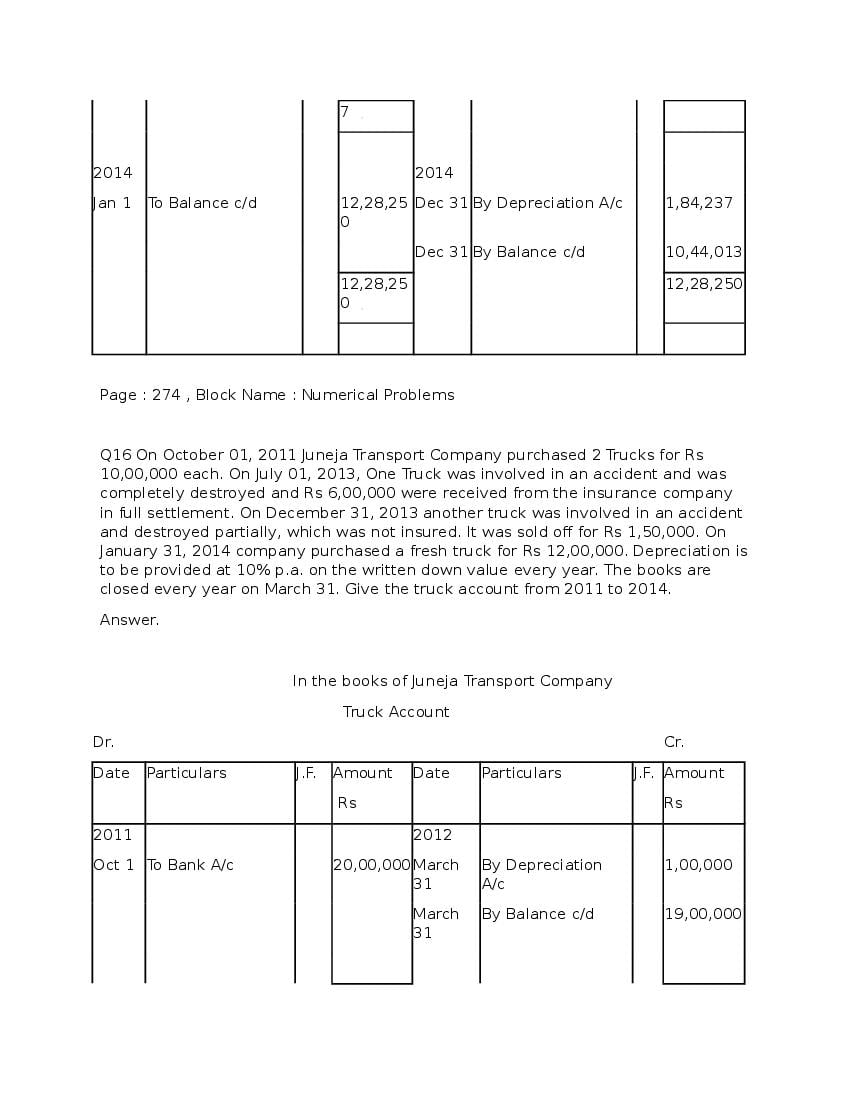
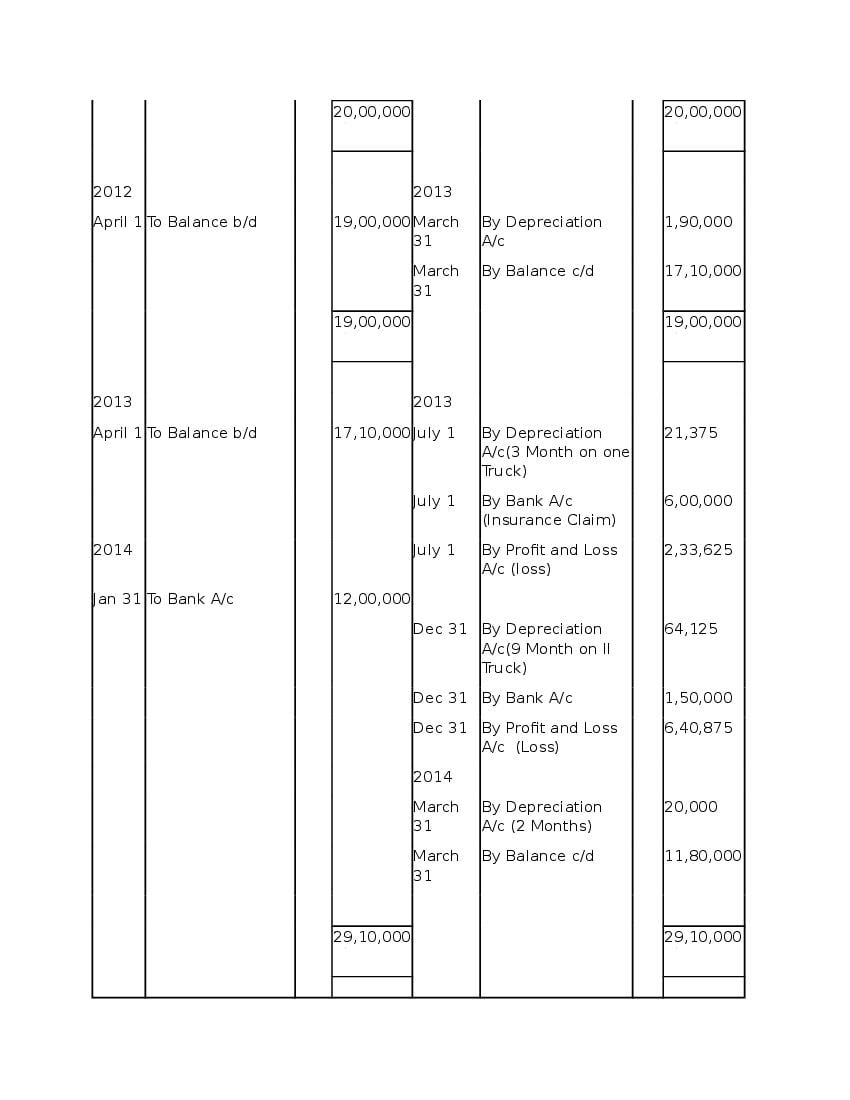
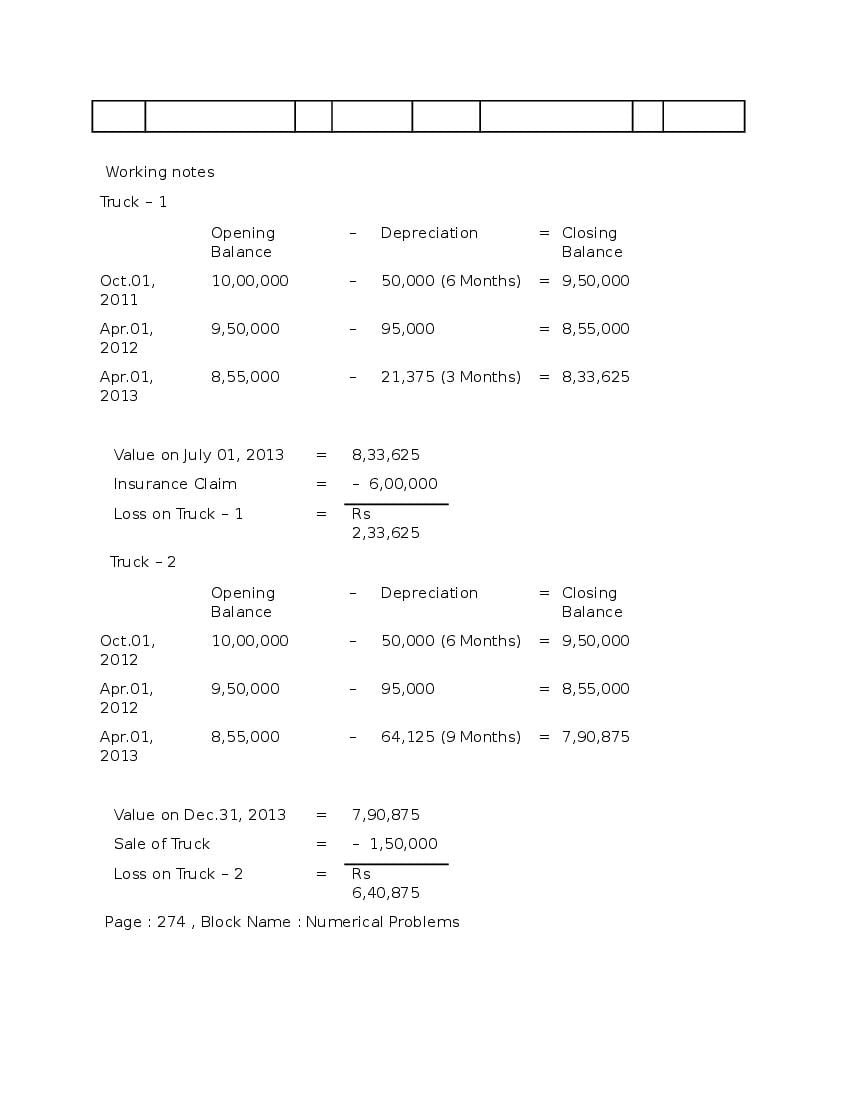
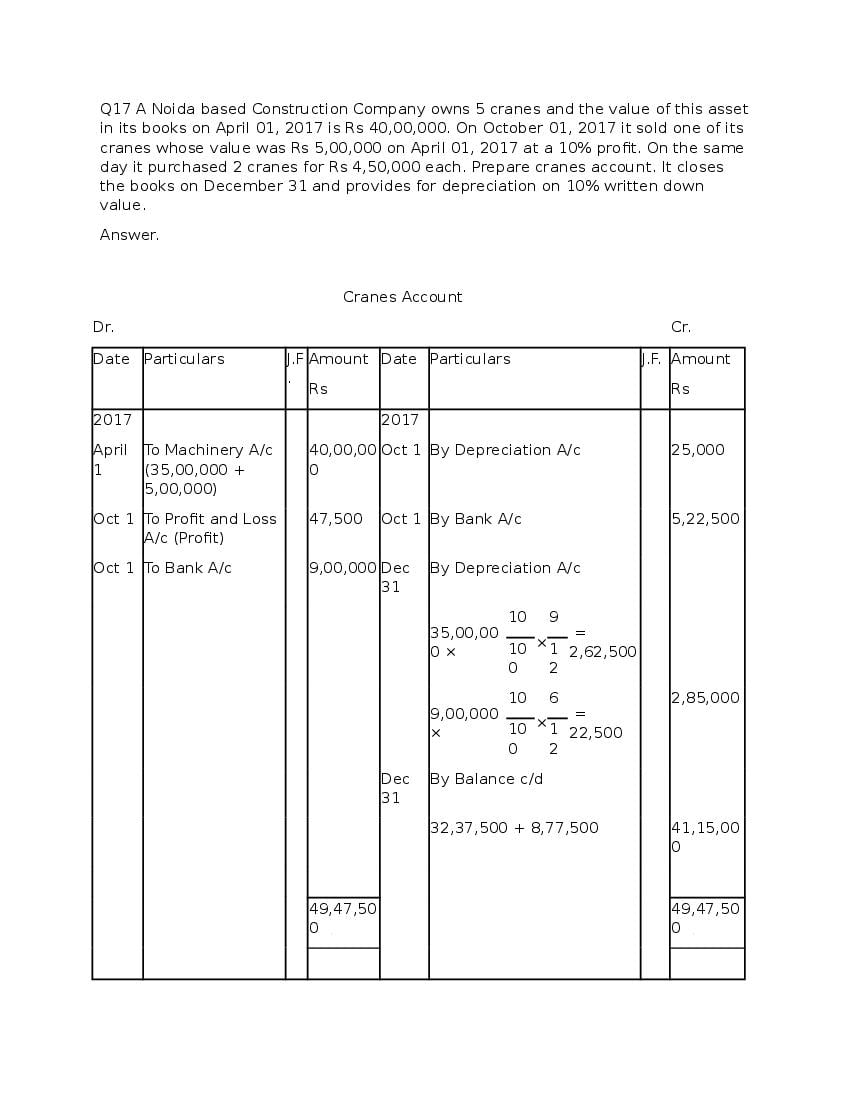
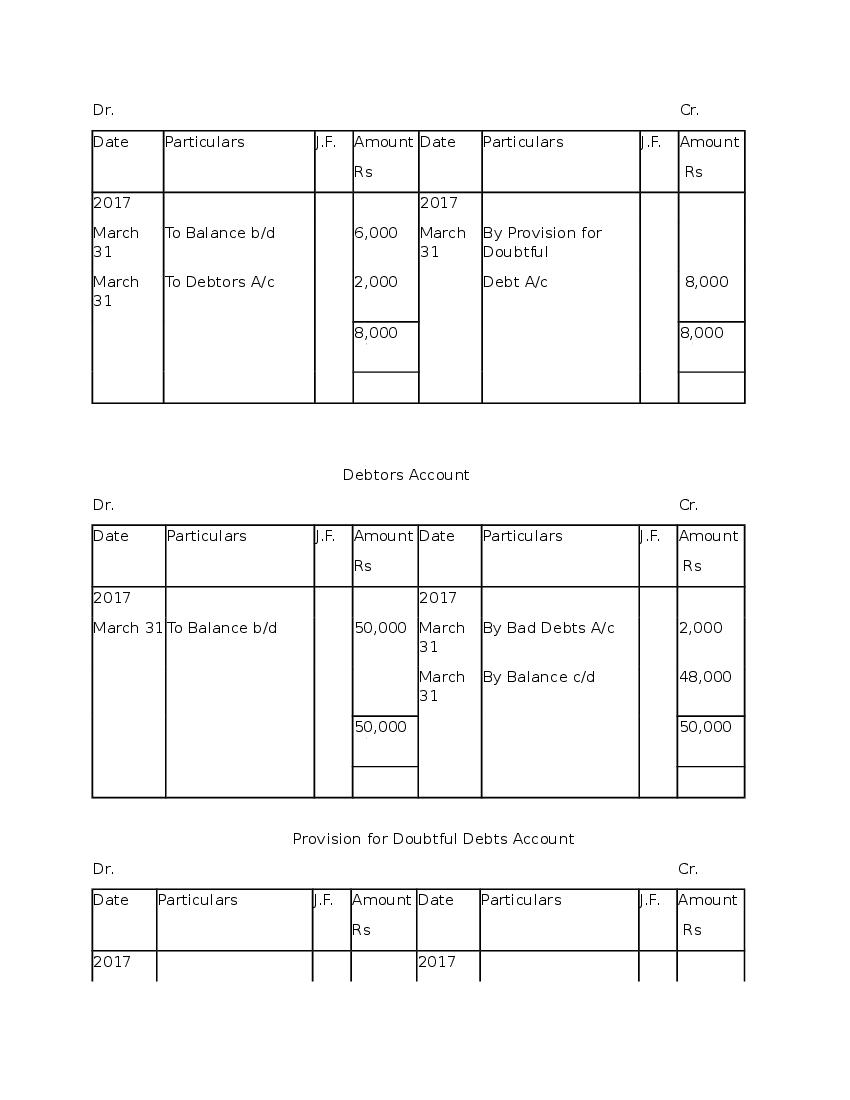
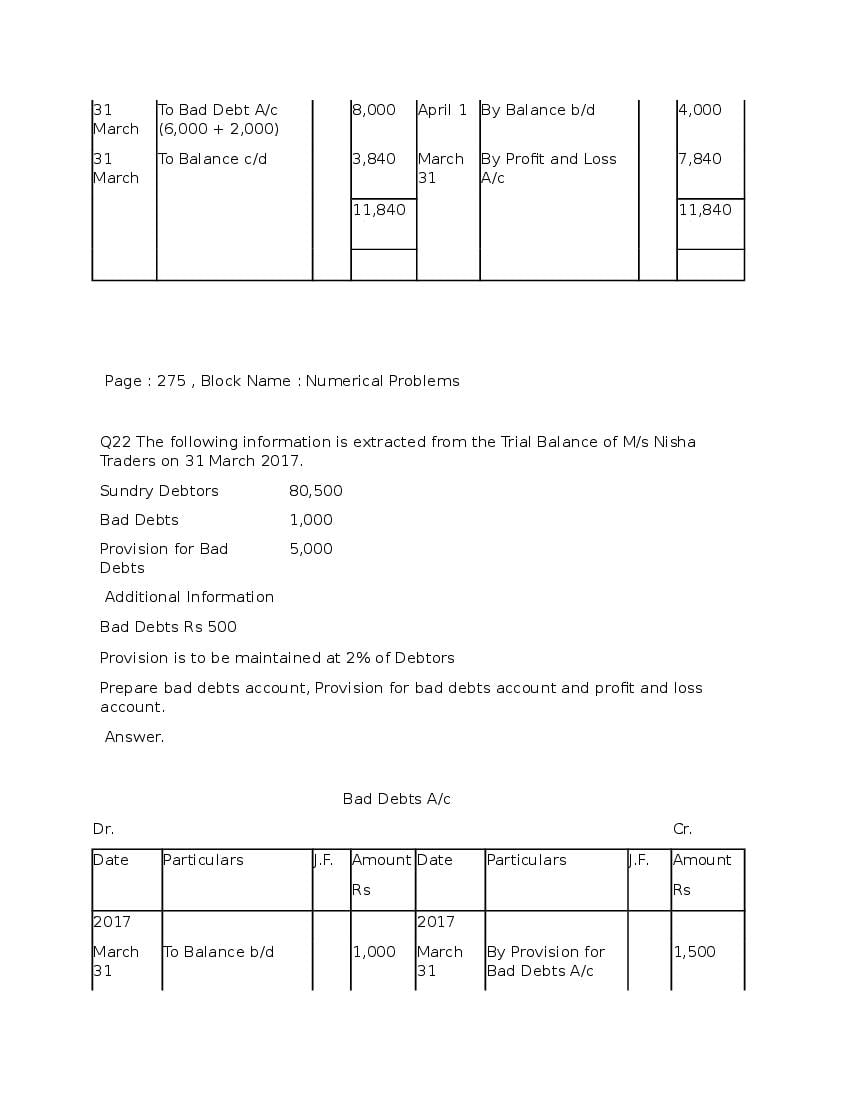
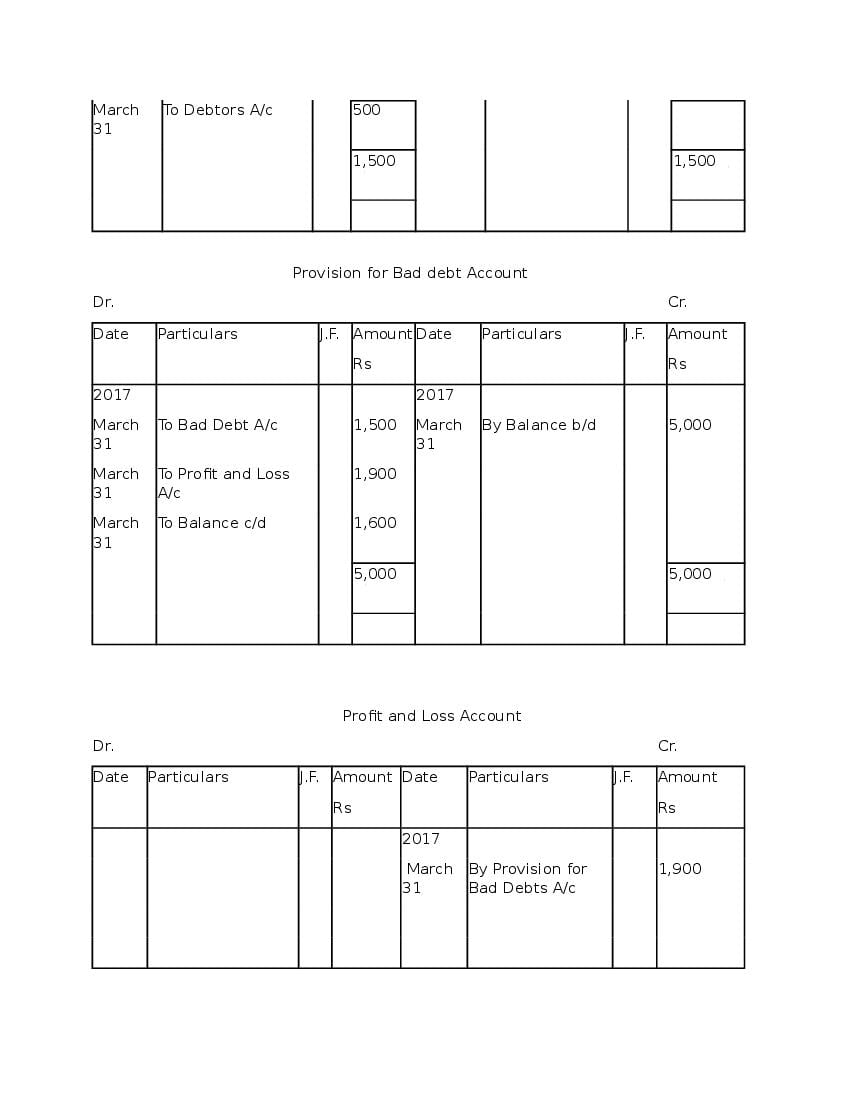
Question & Answer
Q.1: What is ‘Depreciation’?
Ans : Depreciation means fall in book value of depreciable fixed asset because of 1. wear and tear of the asset 2. passage/effux of time 3. obsolescence 4. accident A machinery costing and its useful life is 10 years; so, depreciation is calculated as: Annual Depreciation per annum = Cost of Asset-Estimated Scrap Value/Expected or Estimated life of Asset = 100000/10 = 10,000
Q.2: State briefly the need for providing depreciation.
Ans : The needs for providing depreciation are given below. 1. To ascertain the correct profit or loss: Correct profit or loss can be ascertained when all the expenses and losses incurred for earning revenues are charged to Profit and Loss Account. Assets are used for earning revenues and its cost is charged in form of depreciation from Profit and Loss Account. 2. To show true and fair view of financial statements: If depreciation is not charged, assets will be shown at higher value than their actual value in the balance sheet. Consequently, the balance sheet will not reflect true and fair view of financial statements. 3. For ascertaining the accurate cost of production: Depreciation on the assets, which are engaged in production, is included in the cost of production. If depreciation is not charged, the cost of production is underestimated, which will lead to low selling price and thus leads to low profit. 4. To provide funds for replacement of assets: Unlike other expenses, depreciation is non cash expense. So, the amount of depreciation debited to the profit and loss account will be retained in the business. These funds will be available for replacement of fixed assets when its useful life ends. 5. To meet the legal requirement: To comply with the provisions of the Companies Act and Income Tax Act, it is necessary to charge depreciation.
Q.3: What are the causes of depreciation?
Ans :1. Use of asset: Because of constant use of the fixed assets there exists a normal wear and tear which leads to fall in the value of the assets. 2. Passage of time: Whether assets are used or not, with the passage of time, its effective life will decrease. 3. Obsolescence: Because of new technologies, innovations and inventions, assets purchased currently may become outdated later which leads to the obsolescence of fixed assets. 4. Accident: An asset may lose its value due to mishaps such as a fire accident, theft or by natural calamities and they are permanent in nature.
Q.4: Explain basic factors affecting the amount of depreciation.
Ans : 1. Original cost of asset: The total cost of an asset is taken into consideration for ascertaining the amount of depreciation. The total cost of an asset include all expenses incurred up to the point the asset is ready for use like freight expenses and installation charges. Total Cost: Purchase Price* Freight Expenses+ Installation Charges. 2. Estimated useful life: Every asset has its useful life other than its physical life in terms of number of years and units used by a business. The asset may exist physically but may not be able to produce the goods at a reasonable cost. For example, an asset is likely to lose its useful value within 15 years, its useful life, i.e., life for purpose of accounting should be considered as only 15 years 3. Estimated scrap value: It is estimated as the net realisable value of an asset at the end of its useful life. It is deducted from the total cost of an asset and the difference is written off over the useful life of the asset. For example, Furniture acquired at its useful life is estimated to be 10 years and it is estimated scrap value 10,000. Depreciation per annum= years: 12,000.
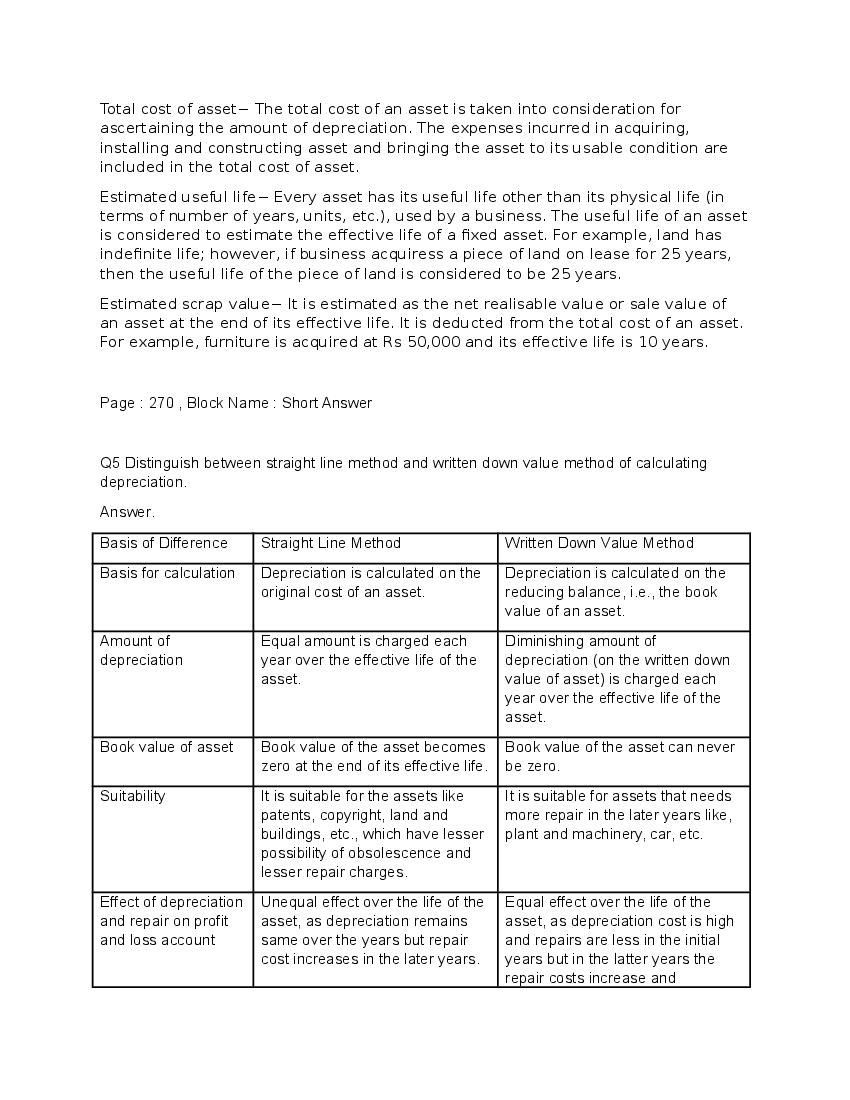
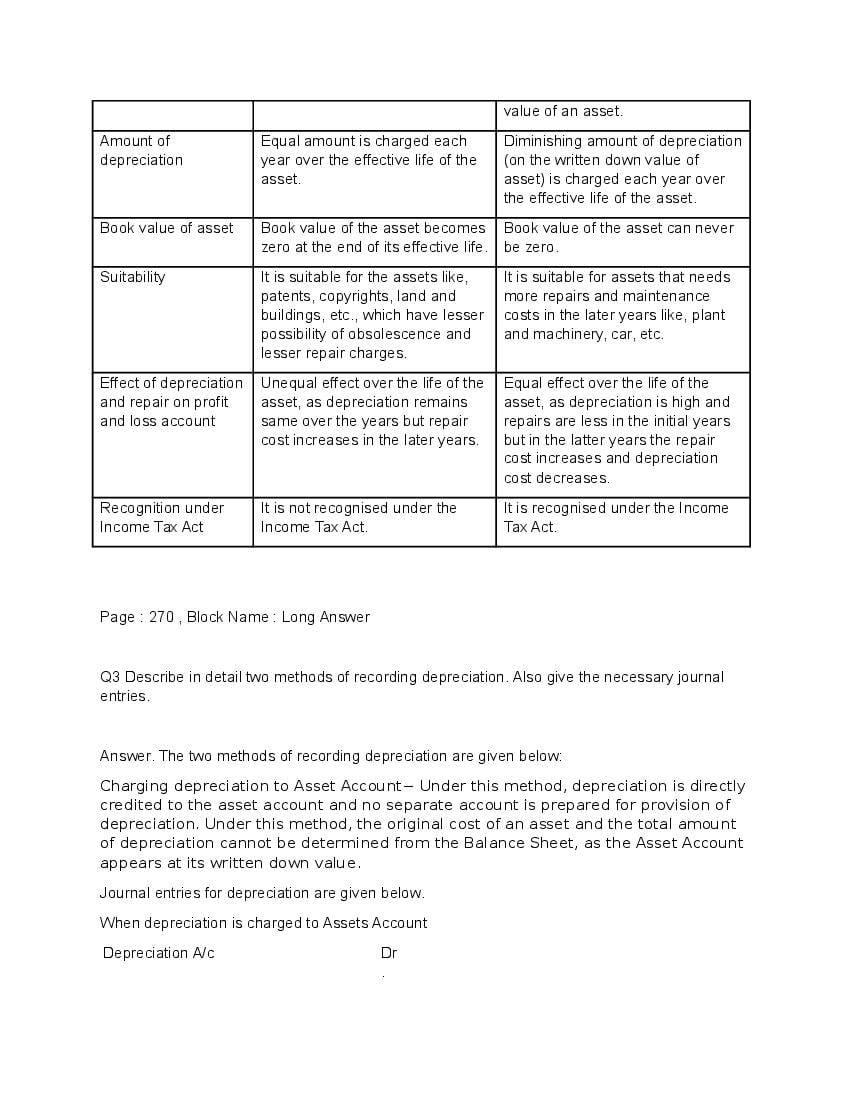
Q.5: “In case of a long term asset, repair and maintenance expenses are expected to rise in later years than in earlier year”. Which method is suitable for charging depreciation if the management does not want to increase burden on profits and loss account on account of depreciation and repair.
Ans : The written down value method is most appropriate to overcome the burden of the profit and loss account because of high depreciation and repair costs over the years of the asset. The cost of depreciation reduces and the repair and maintenance expenses increase over the yea* However, the entire burden will not get ease to the management.
NCERT / CBSE Book for Class 11 Accountancy
You can download the NCERT Book for Class 11 Accountancy in PDF format for free. Otherwise you can also buy it easily online.
- Click here for NCERT Book for Class 11 Accountancy
- Click here to buy NCERT Book for Class 11 Accountancy
All NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Economics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 History
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Geography
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Sociology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Statistics
All NCERT Solutions
You can also check out NCERT Solutions of other classes here. Click on the class number below to go to relevant NCERT Solutions of Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12.
| Class 4 | Class 5 | Class 6 |
| Class 7 | Class 8 | Class 9 |
| Class 10 | Class 11 | Class 12 |
Download the NCERT Solutions app for quick access to NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves. It will help you stay updated with relevant study material to help you top your class!
The post NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions And Reserves appeared first on AglaSem Schools.
from AglaSem Schools https://ift.tt/3hiW3U1
https://ift.tt/3e5jHng https://ift.tt/3e5jHng










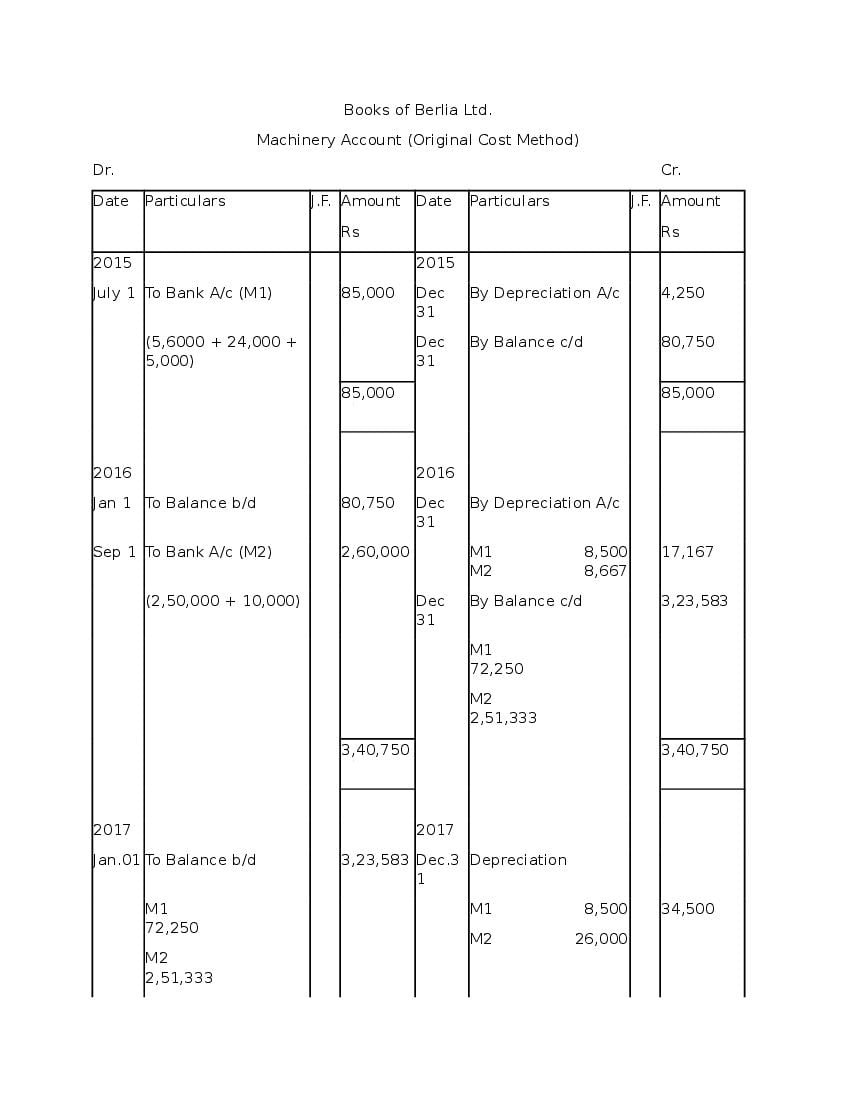
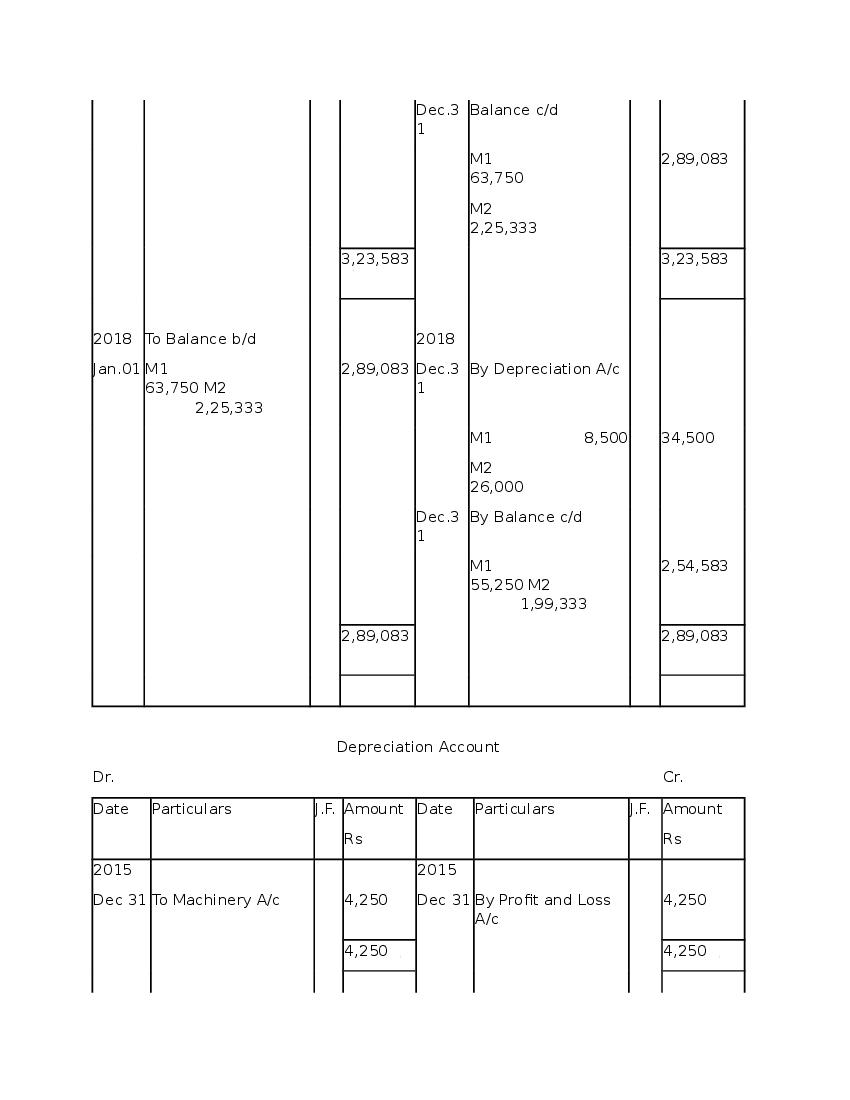
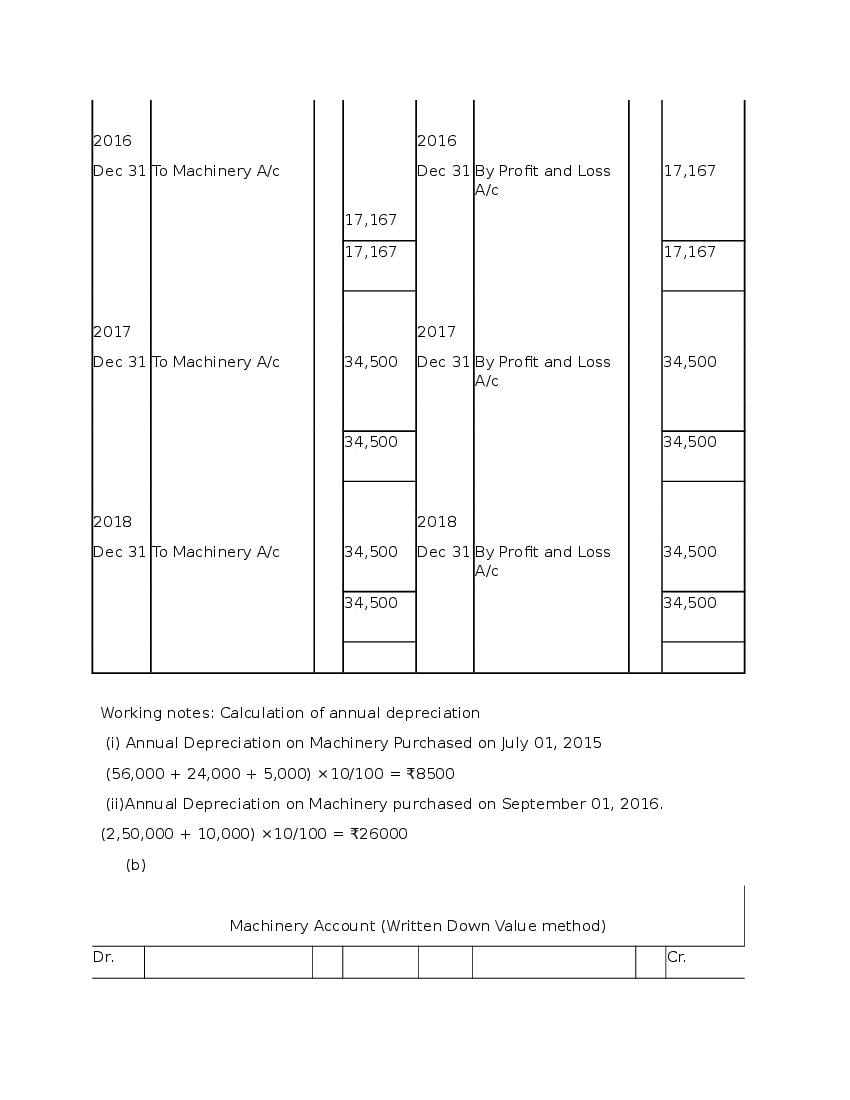
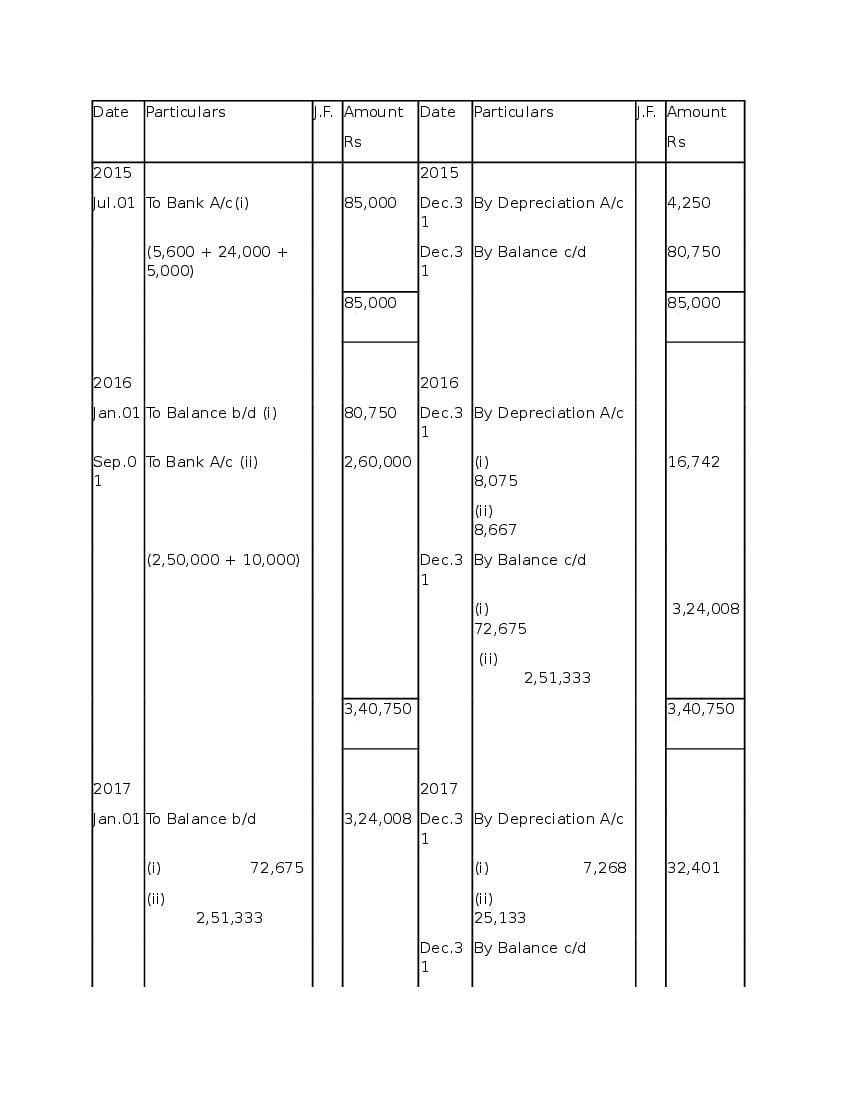
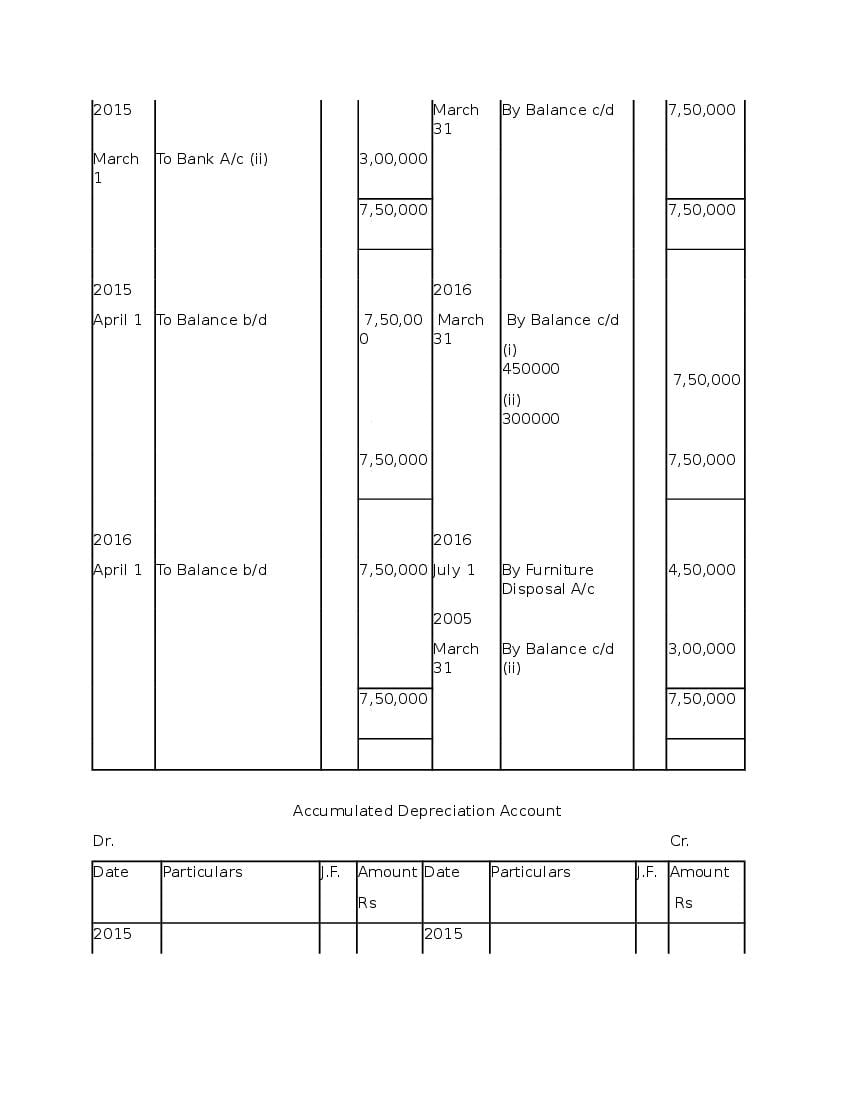
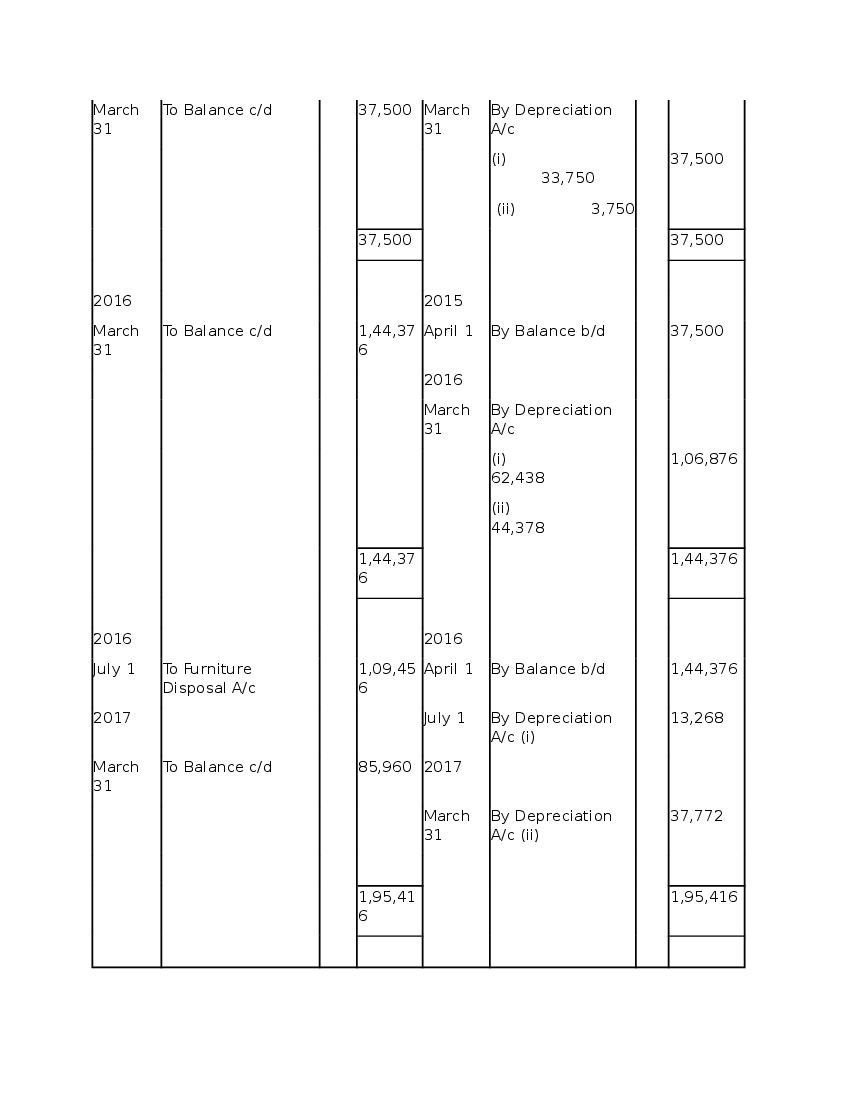
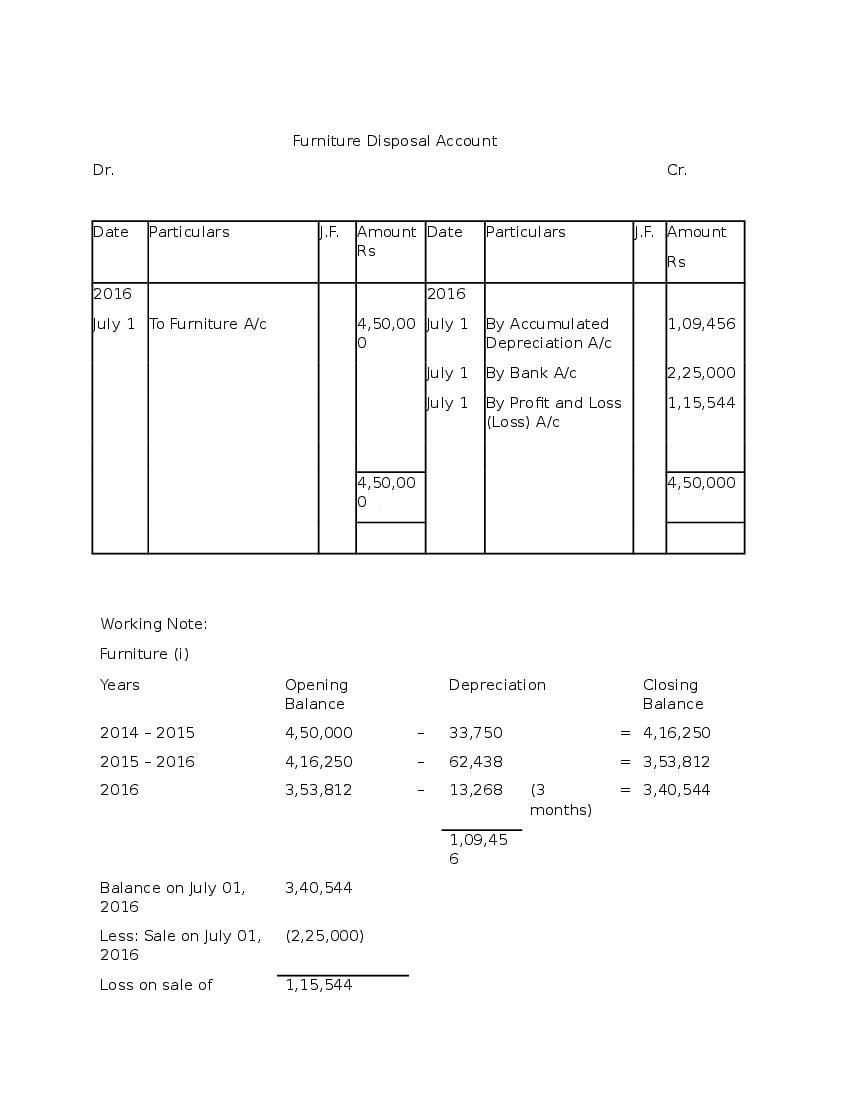
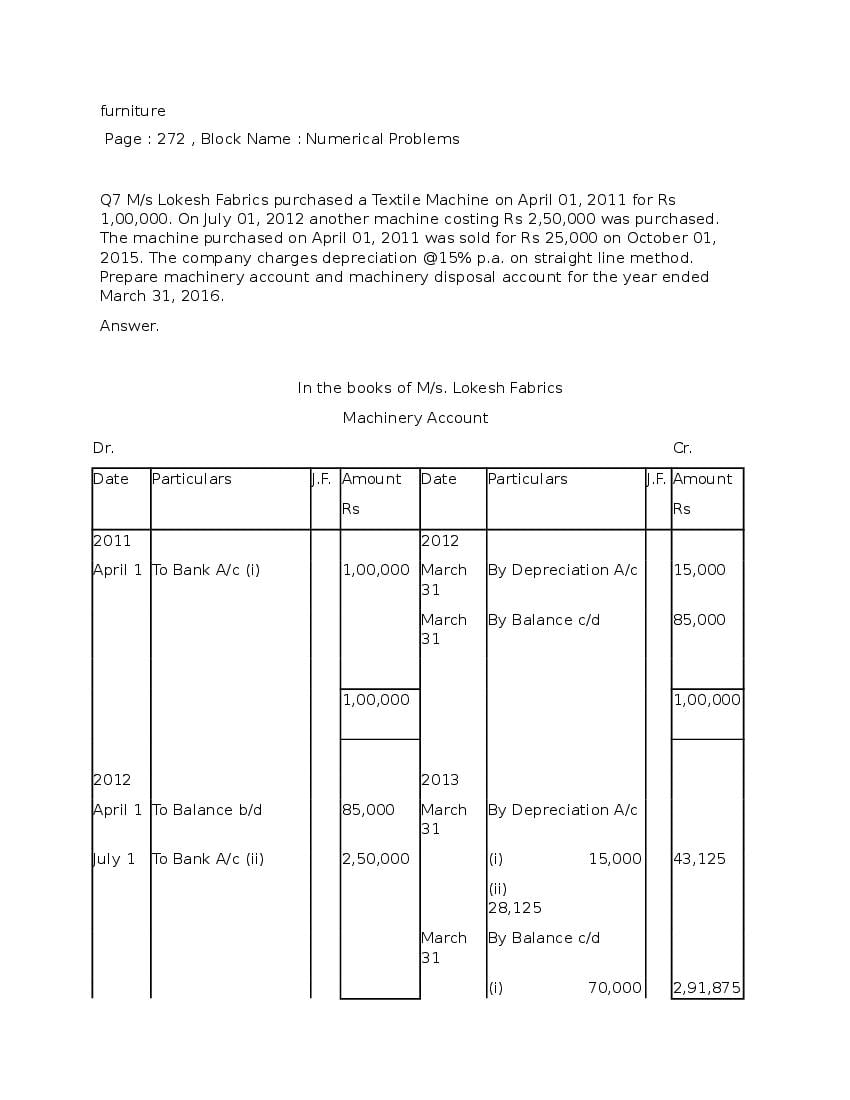
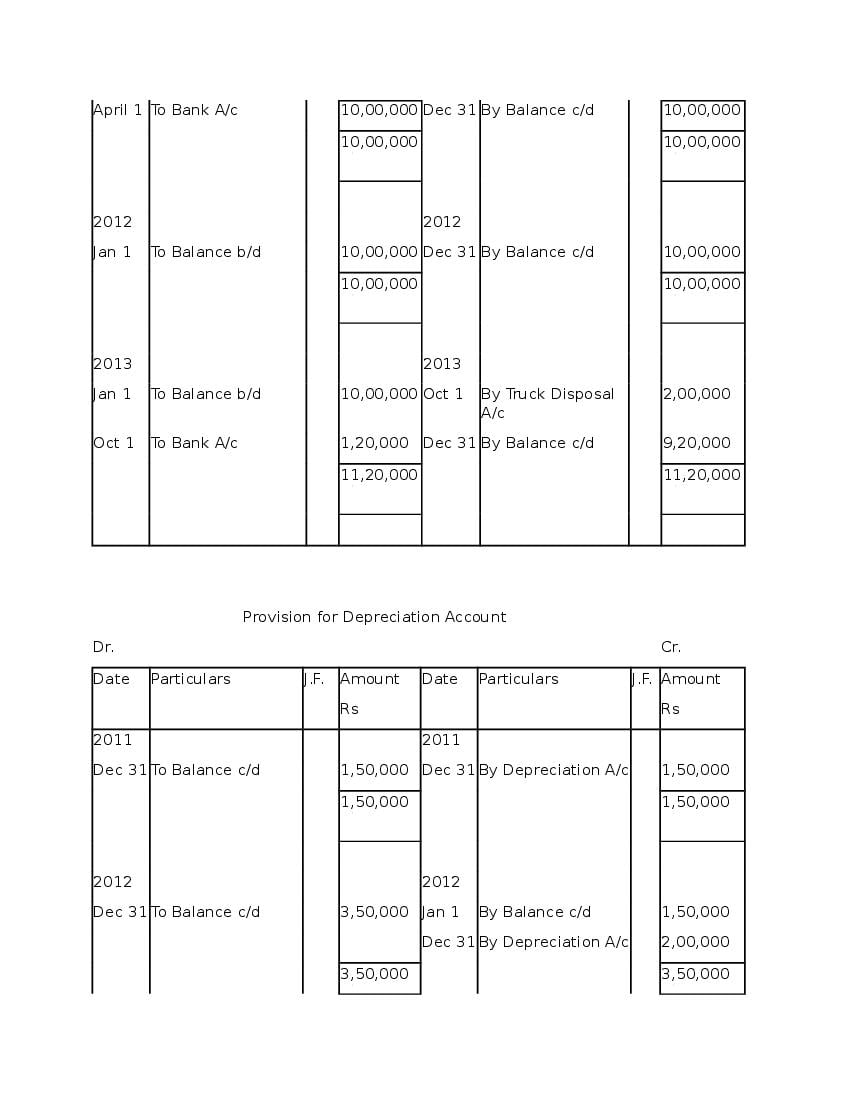
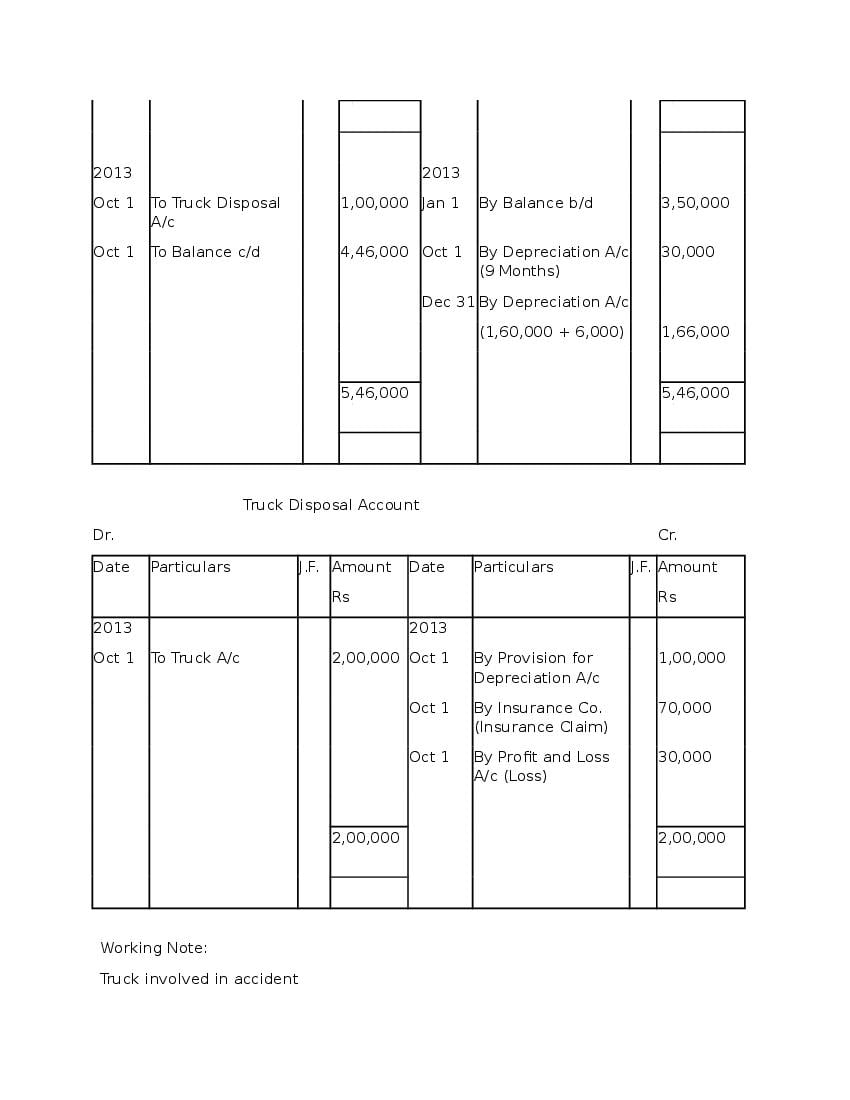
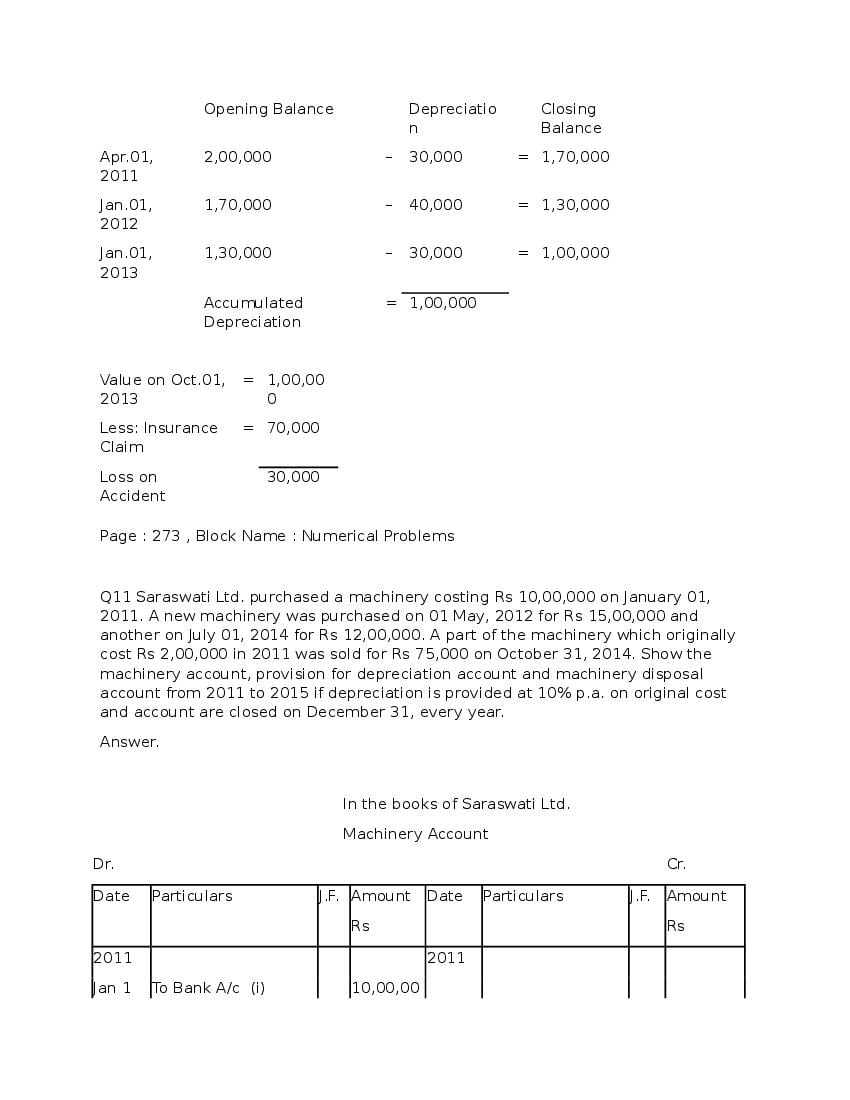
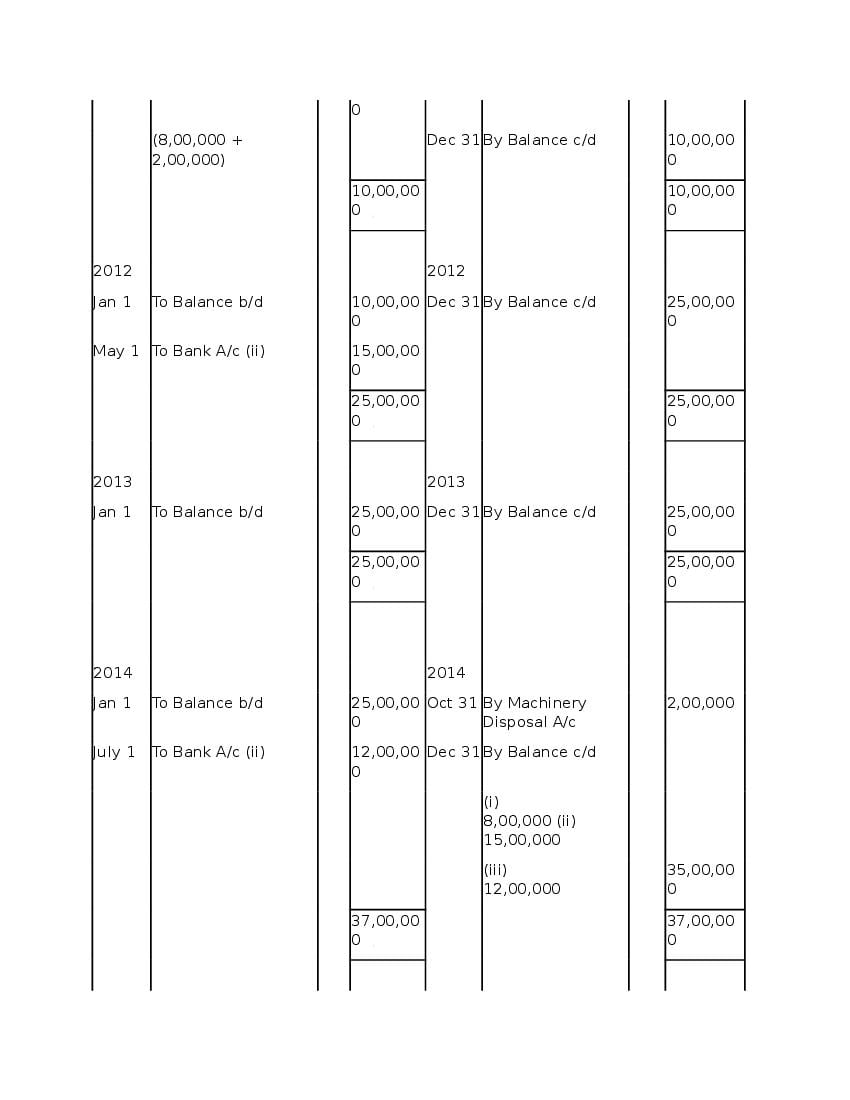
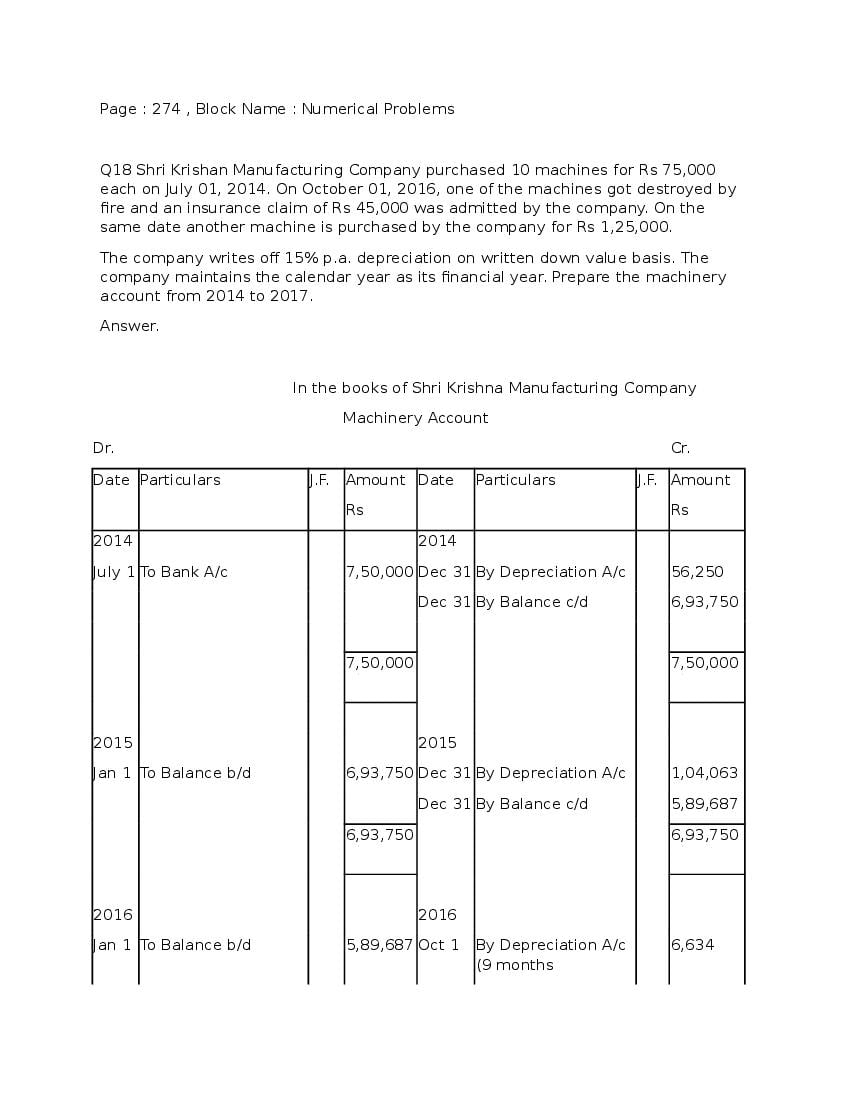
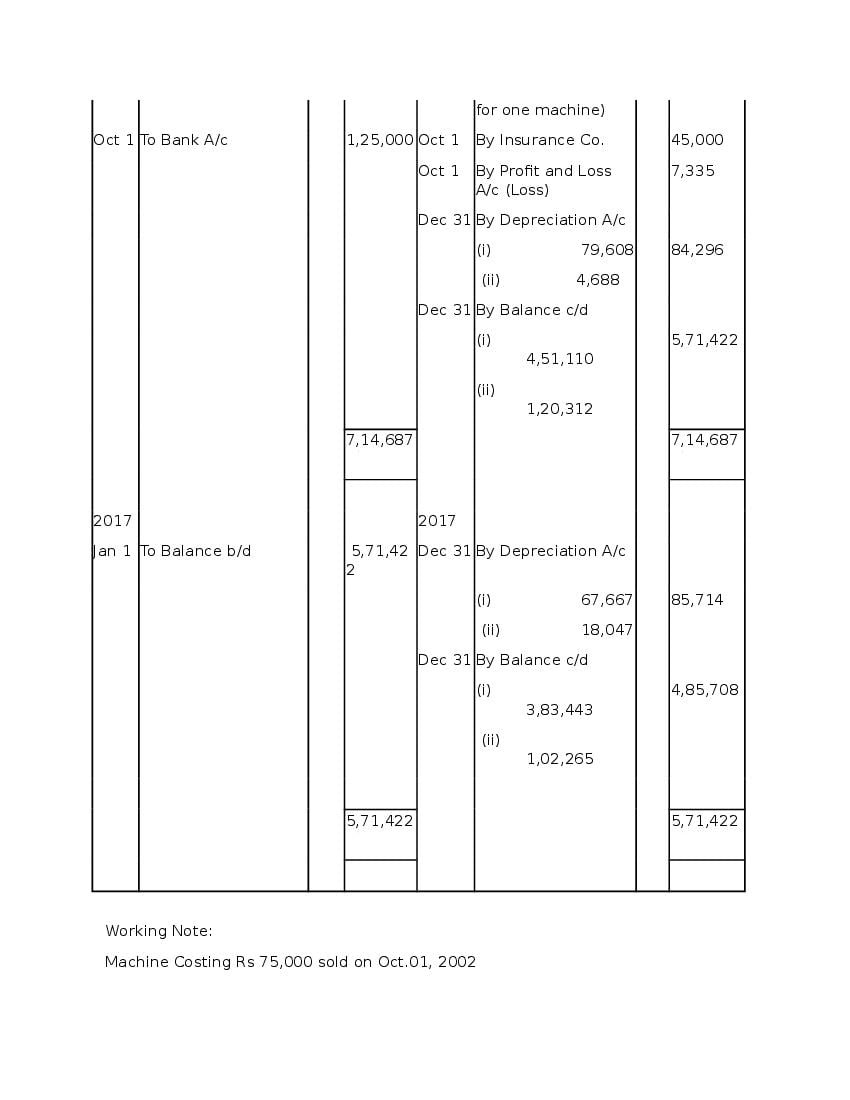
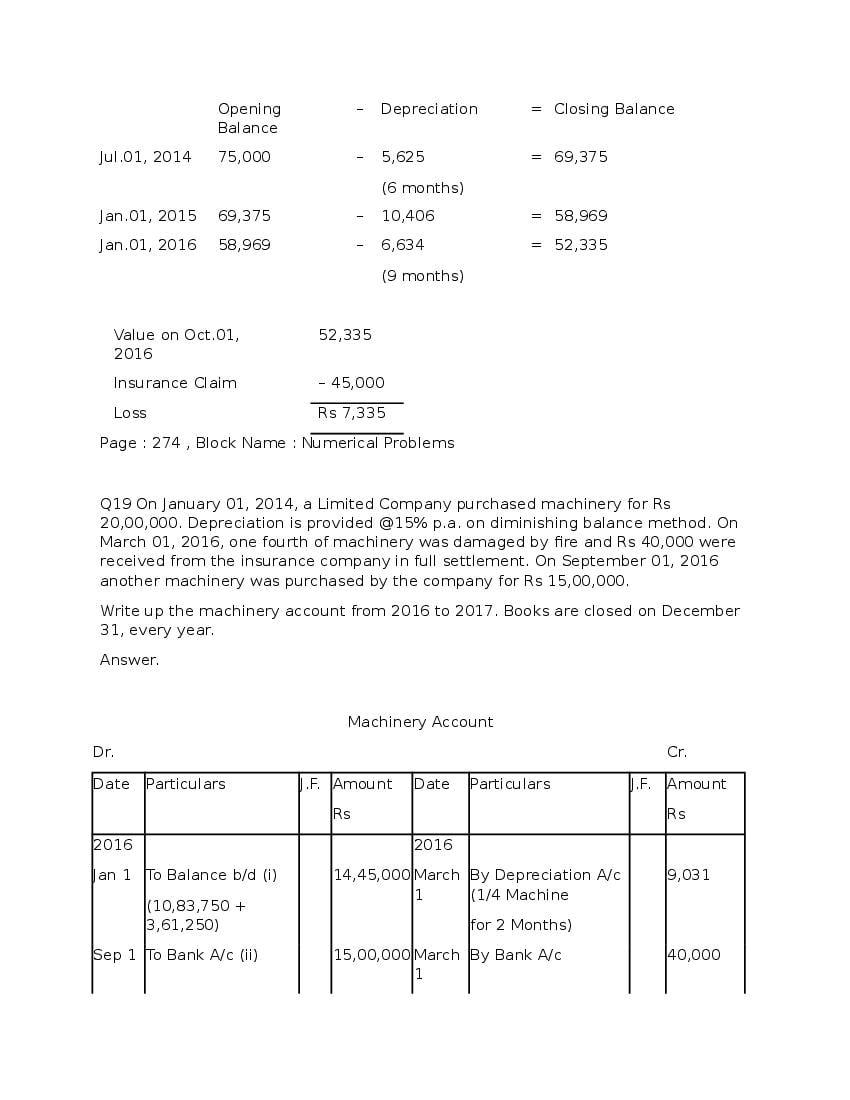
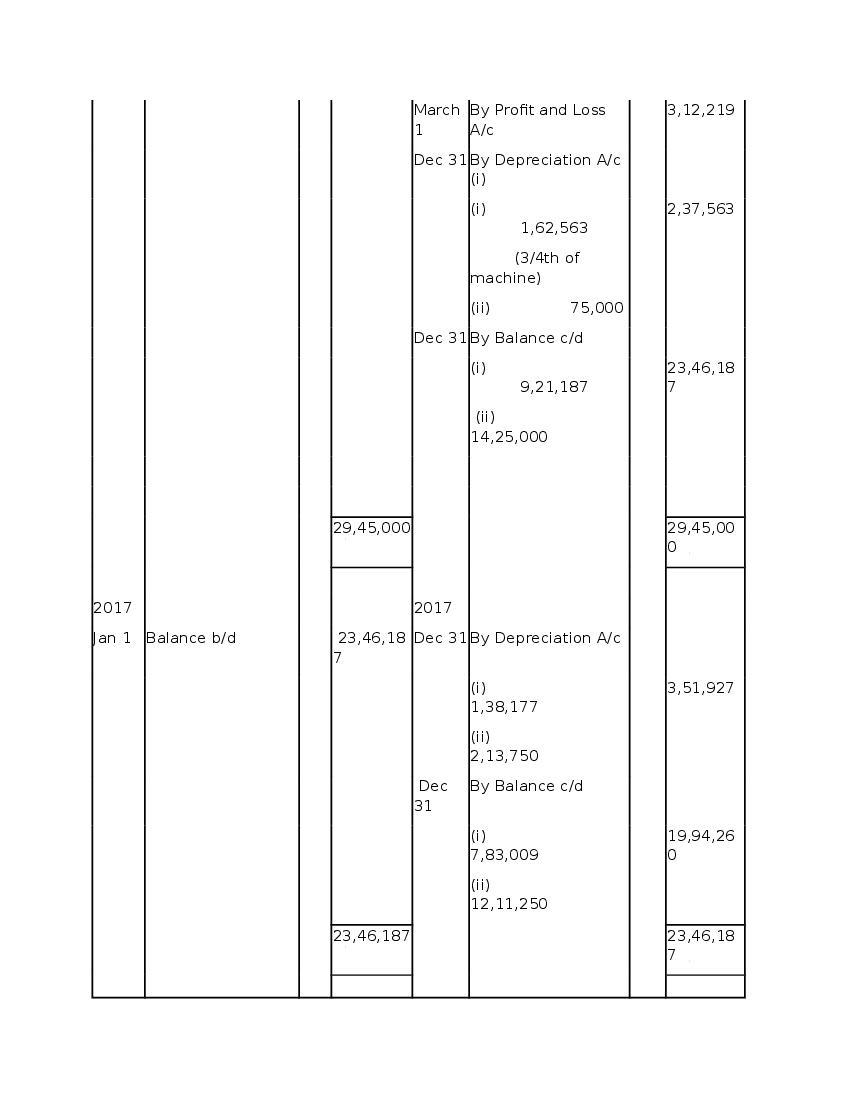

Post a Comment